Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
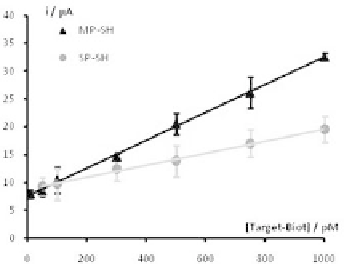
9.4.4.2 Results
After verifying that the presence of a certain quantity of not
complementary target strand does not concern the analytical signal
obtained by the complementary strand a simultaneous calibration
plot for bothtarget sequences iscarried outFig. 9.18.
The
S. pneumoniae
targetstrandshowalinearrelationshipofthe
analytical signal with the concentration of the biotinylated target
strand in the range comprised between 50 pM and 1 nM. The
detection limit, calculated as the concentration corresponding to a
signal that is 3 times the standard deviation of the intercept, was
found to be 34 pM.
The
M. pneumoniae
target strand show a linear relationship
of the analytical signal with the concentration of the biotinylated
target strand in the range comprised between 10 pM and 1 nM. The
detection limit, calculated as the concentration corresponding to a
signalthatisthreetimesthestandarddeviationoftheintercept,was
found to be5 pM.
It has been seen that the presence of another bacteria in the
sample does not concern significantly the analytical signal obtained
for an individual bacteria (though the analytical signal diminishes a
bit), this indicates that simultaneous calibrations or identifications
of several bacteria can bedone.
Later,identificationofPCRproductsofthesebacteriawascarried
out. Dilution of the PCR product has been studied, and a 1:4
Figure 9.18.
Simultaneous calibration plots for
S. pneumoniae
and
M.
pneumoniae
obtainedwithgoldnanostructureddualscreen-printedcarbon
electrodes.