Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
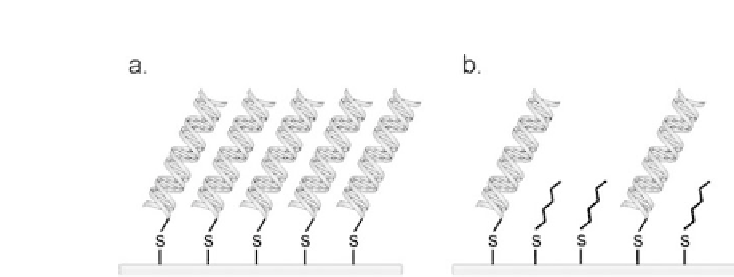
Figure 7.2.
(a) DNA film formed by self-assembly of thiol containing ODN
onto Au surfaces. (b) DNA film formed by self-assembly followed by a
dilution step with an alkylthiol diluents.
probes is required to control repulsion of the targets strands and
the steric effects between the probe strands on the surface [8].
Functionalizedsurfacescanalsobeusedforcovalentattachment
of modified DNA strands. For instance, DNA molecules were cova-
lently immobilized onto carbon paste electrode surfaces that was
activated using a carbodiimide (1-[3-(dimethylamino)-propyl]-3-
ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride) and
N
-hydroxysulfosuccinimide
[9].Inanothercovalentattachmentstrategy,individualDNAstrands
wereattachedtoacarbonnanotube(CNT)layersupportedonagold
surface. Again, amide coupling between the carboxylic acid groups
ontheCNTsandthe5'-aminogroupofDNAresultedintheformation
of a stable amide linkage and the resulting conjugate proved stable
to the electrochemical experiment[10].
7.2.2
Adsorption
Adsorption is the simplest method of immobilization as it does not
involve the formation of covalent bond formation between the ODN
and the surface (see Fig. 7.1b). Instead, it relies on electrostatic
interactions between negatively charged sugar-phosphate skeleton
ofDNAandpositivelychargedelectrodesurfaceand/orinteractions
involving the nucleobases and the surface. Physical adsorption is
often achieved on electrochemical oxidized carbon electrodes [11-
14] (HOPGE, GCE, CPE) and less often on gold [15] or ITO [16]
surfaces. For examples, cationic polymers, such as chitosan, have