Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Pt-NPsareusedascatalystsforelectrochemicalhydrogenperox-
ide (H
2
O
2
) detection, where they act as modifiers of the electrode
surface and electrocatalyze the oxidation of H
2
O
2
observed by
a lower oxidation peak potential when compared with the bulk
platinumelectrode[30].AstheH
2
O
2
isaproductofmanyenzymatic
reactions, this electrode has a vast potential application as an
electrochemical biosensorformany substances[15].
Pt-NPs have also been used as catalysts in gas sensors like nitric
oxide (NO) sensor making use of the electrocatalytic effect in the
oxidation of this specie [31]. In conjugation with carbon nanotubes
(CNTs) and glutaraldehyde, Pt-NPs also allowed the development of
acarbon-basedelectrodeasasensorforglucose,inasimilarsystem
as oneof the reported H
2
O
2
sensors [13].
Regarding its application in DNA sensors, Polsky
et al.
[10]
used nucleic acid functionalized Pt-NPs as catalytic labels to
amplify the electrochemical detection of both DNA hybridization
and aptamer/protein recognition. The assay was based on the
catalytic effect of the Pt-NPs on the reduction of H
2
O
2
to H
2
O, using
gold slides as electrodes. The amperometric measurement of the
electrocatalyzed reduction of H
2
O
2
detected DNA with a LOD of
1
×
10
−
11
M.
N. Zhu
et al.
[32] reported in 2005 the use of Pt-NPs combined
with nafion-solubilized MWCNTs as electrode-surface modifiers
forfabricatingsensitivity-enhancedelectrochemicalDNAbiosensor.
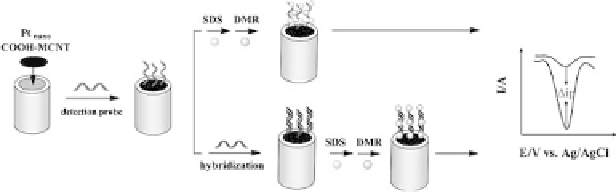
The hybridization events were monitored by DPV measurements
of the intercalated daunomycin (Fig. 5.5). Due to the ability of
MWCNTs to promote electron-transfer reactions and the high
Figure 5.5.
Schematic representation of the electrochemical detection of
DNAhybridizationbasedonPt-NPscombinedwithMWCNTs(adaptedfrom
Ref. 32 with permission). See also ColorInsert.