Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
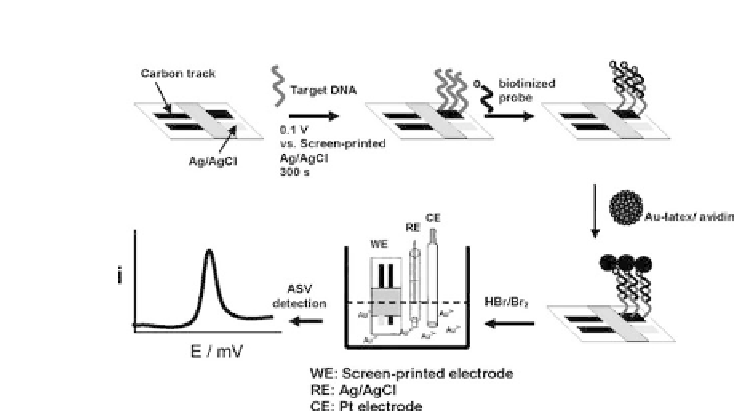
Figure 4.10.
Schematic representation of the procedure for detection of
DNA hybridization using Au-NP-coated latex labels [65] (reprinted with
permission of acs).
Pinijsuwan
et al.
[65] loaded streptavidin-coated latex particles
with biotin-coated Au-NPs so as to increase the quantity of Au-NPs.
Then, they attached the latex particles to biotinylated DNA probes
for
E. coli
previously hybridized to a DNA-modified SPE (Fig. 4.10).
The detection step involved the immersion of the modified SPE in
aHBr/Br
2
solution, and further differential pulse anodic stripping
voltammetry (DPASV) of Au
3
+
ions. Following this methodology, a
detection limitof 0.5 fM wasachieved.
The procedures described by Castaneda
et al.
[66] and by
Zheng
et al.
[67] were based on the detection of Au-NPs through
their electrochemical oxidation to AuCl
4
at
+
1.25 V (vs. Ag/AgCl),
followed by a DPV scan resulting in an analytical signal due to
the reduction of AuCl
4
at
+
0.4 V. This method was applied for
the detection of DNA hybridization using two different approaches
[66]. The first one consisted of hybridization between a capture
DNA strand linked with paramagnetic beads and a target DNA
strand related to BRCA1 breast cancer gene which was coupled
with streptavidin-Au-NPs. The second design was based on a
sandwich assay where a cystic fibrosis related DNA strand was
used as the target and sandwiched between two complementary