Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
area, allows a larger number of short DNA sequences to be bound,
leading to a substantial amplification of signals for ultrasensitive
detection.
4.2.2
Gold Nanoparticles: Metallic Oxide Composites
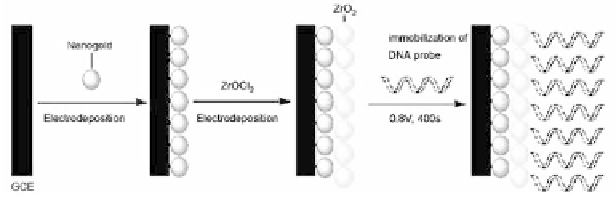
Metallic oxides have been used in combination with gold nanopar-
ticles to prepare electrode surfaces with improved stability and/or
response capacity for DNA detection. Among them, zirconia (ZrO
2
)
has been used in various applications due to its thermal stability,
chemical inertness, lack of toxicity, and a
nity for the groups
containing oxygen. Thus, it is an ideal candidate material for the
immobilization of biomolecules with oxygen groups. The approach
used for the preparation of an electrochemical DNA biosensor
based on zirconia and gold nanoparticles is depicted in Fig. 4.4. A
gold nanoparticle film was electrodeposited onto a glassy carbon
electrode, and then a zirconia thin film was prepared on the Au-
NPs/GCE by cyclic voltammetry in an aqueous electrolyte of ZrOCl
2
and KCl. DNA probes were attached onto the ZrO
2
/Au-NPs/GCE
due to the strong binding of the phosphate group of DNA with the
zirconia film and the excellent biocompatibility of nanogold with
DNA [17].
Thin gold films deposited by low pressure gold sputtering
or electrochemical deposition can provide a highly sensitive and
reproducible electrode for the preparation of DNA biosensors
without the requirement of the cleaning step. However, the thin
gold film directly sputtered on a substrate very easily peels off
Figure 4.4.
Schematic representation of the DNA immobilization on a
ZrO
2
/ Au-NPs/GCE [17](adapted with permission of Elsevier).