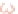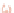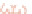Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
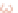
Ganglionic cells
Fovea
Bipolar cells
Photoreceptor
Pigmented epithelium
Cones
Rods
Figure 10.7
Histological characteristic of the retina.
Binocular
visual field
Monocular portion
of visual field
Monocular portion
of visual field
Left visual
field
Right visual
field
Left monocular visual field
Right monocular visual field
Left retina
Right retina
S
S
Superior (S)
S
Temporal
(T)
Nasal
(N)
T
T
T
N
Fixation
point
Fovea
Inferior (I)
I
I
I
Figure 10.8
Projection of the visual fields onto the left and right retinas. Projection of an image onto the surface of the retina.
The passage of light rays through the optical elements of the eye results in images that are inverted and left-
right reversed on the retinal surface. Retinal quadrants and their relation to the organization of monocular and
binocular visual fields as viewed from the back surface of the eyes. Vertical and horizontal lines drawn through
the center of the fovea define retinal quadrants (bottom). Comparable lines drawn through the point of fixation
define visual field quadrants (center). Color coding illustrates corresponding retinal and visual field quadrants.
The overlap of the two monocular visual fields is shown at the top.