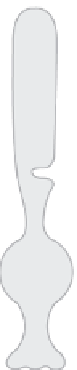Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
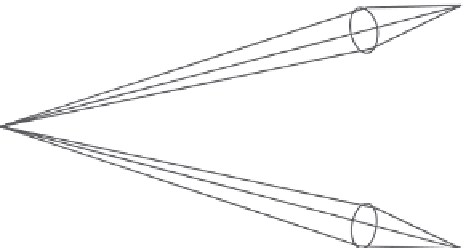
Fovea
Fovea
FIgUre 10.3
Convergence.
e rod cell
e cone cell
Outer segment
Inner segment
Nucleus
Synaptic ending
FIgUre 10.4
Cone and rod cell.
Not everybody notices that in the retina the receptors are covered with neurons, except
for the fovea, where the neurons are laterally shifted to avoid any interference on the optic
pathway of the light.
It is anatomically possible to distinguish three different areas in the retina (Figure 10.6):
1. The blind spot, where the optic nerve emerges;
2. The macula, with the fovea in the middle, the area where the maximal visual acu-
ity can be detected; and
3. The periphery, defined in function as the angular distance from the fovea.
For the histological characteristics of the retina and for the connections between rods
and cones and the first- and second-order neurons, the resolution capability of the retina
is different in the various areas (Figure 10.7).