Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
The following support data security and access control to scientific data
during their life cycle: data acquisition (experimental data), initial data filter-
ing, specialist processing, research data storage and secondary data mining,
data and research information archiving.
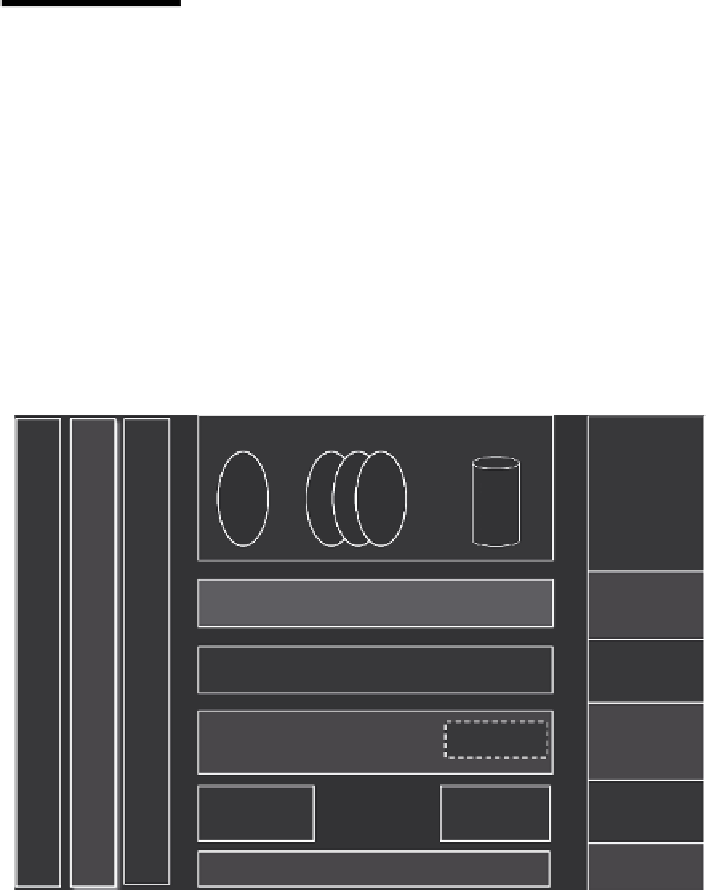
2.5 Scientific Data Infrastructure Architecture Model
The proposed generic SDI architecture model provides a basis for building
interoperable data or project-centric SDI using modern technologies and
best practices. Figure 2.4 shows the multilayer SDI architecture for e-science
(e-SDI) that contains the following layers:
Layer D1:
Network infrastructure layer represented by either the general-
purpose Internet infrastructure or dedicated network infrastructure
Layer D2:
Data centers and computing resources/facilities
Layer D3:
Infrastructure virtualization layer represented by the cloud/grid
infrastructure services and middleware supporting specialized scien-
tific platform deployment and operation
Layers
Scientific/User Applications
Layer B6
Scientific
Applications
Layer B5
Access and
Delivery Layer
Federated Access and Delivery Infrastructure (FADI)
Policy Management and collaborative Groups Support
Layer B4
Scientific Platform
and Instruments
Shared Scientific Platform and Instruments
(specific for scientific area, also Grid based)
Cloud/Grid Infrastructure
Virtualization and Management
Middleware
Layer B3
Infrastructure
Virtualisation
Middleware
security
Layer B2
Datacenter and
Computing Facility
Compute
Resources
Storage
Resources
Layer B1
Network
Infrastructure
Network infrastructure
FIGURE 2.4
The proposed SDI architecture model.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search