Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
(a) Temperature parameters for AMD server
Whole SPEC CPU execution
(b) Power consumption for AMD server
Whole SPEC CPU execution
60
240
220
50
200
180
40
160
140
30
120
0
10
20
30
40
50
0
10
20
30
40
50
Time (10
3
sec)
Time (10
3
sec)
CPU0
Inlet
Outlet
Server Power
(c) Temperature parameters for AMD server
Zoom in one benchmark
(d) Power consumption for AMD server
Zoom in one benchmark
60
250
50
200
X: 50
Y: 48
40
150
30
20
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
3000
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
3000
Time (sec)
Time (sec)
Server Power
CPU0
Inlet
Outlet
FIGURE 12.4
Temperature and power values for AMD server under SPEC CPU 2006 workload.
jointly computational and cooling perspective. However, these works do not
generally apply their solutions in a real scenario.
Our proposal considers not only the heterogeneity that comes from the
use of different servers inside a data center facility but also the use of the
heterogeneous elements that compose the MCC scenario outside the facil-
ity. We leverage the use of nonoptimal lightweight distributed allocation
algorithms based on the use of satisfiability modulo theory (SMT) formulas
outside the facility. We combine this allocation with MILP-based problems
in the data center facility and envision the use of genetic algorithms (GAs) to
solve larger resource management problems. We apply these algorithms to
real data collected from a completely monitored data room, obtaining inlet
and outlet server temperature values, CPU temperatures, server fan speed,
server power consumption, and cooling power. Figure 12.4 shows the tem-
perature and power traces obtained from an AMD Sunfire V20Z server when
executing tasks of the SPEC CPU 2006 benchmark [35].
12.5.1 SMT Solvers
An SMT solver decides the satisfiability of complex formulas in theories such
as arithmetic and uninterpreted functions with equality. An SMT solver is a



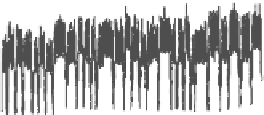










Search WWH ::

Custom Search