Graphics Programs Reference
In-Depth Information
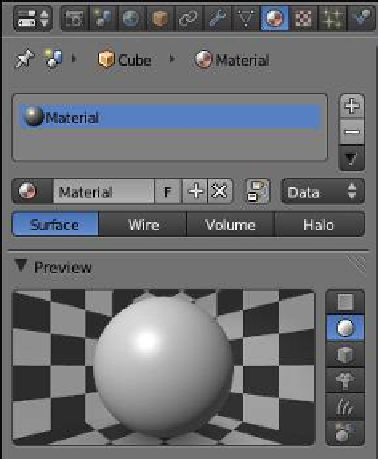
material applied to it, as seen in the properties window - “Ma-
terial” button; the material displays as the default gray color. At
this point, it is worth taking a look at what we have in terms
of the material. Look at the properties window - “Material”
button. The preview tab shows a sphere with the gray color
and a material named “Material” is selected and assigned to
the material slot (Figure 18.8). The material slot is linked to the
selected cube object in the 3D window, which renders as the
gray color. Clicking on the “Browse ID data” button shows the
material cache with only the material named “Material” stored
in it.
Figure 18.8
“Browse ID data” button
18.3.1 What Is a Material?
A material in Blender is a bunch of data that tells the program
to display the surface of an object in a certain way (i.e., gray
in color, reflecting a certain color under a light source, having
bumps or spots, etc.). The data is grouped together in a block
called a data block.
18.3.2 Data Blocks
If you change the 3D window to the outliner window in data
blocks mode, you will see the “Materials” data block as one of the entries (Figure 18.9).
Click on the + sign next to “Materials” to see the data block for the material named “Mate-
rial.” Note that Blender's default screen arrangement has an outliner window in the upper
RH side of the screen—as I mentioned before, this window is an abridged version of the full
outliner window. It's worth mentioning here that you can change the name of the material
in the name slot in the data block. Just click in the slot, delete, and retype a new name and
the name change will be reflected in the properties window - “Material” button. This is very
useful when creating multiple materials.
Figure 18.9