Graphics Programs Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 14.36
Figure 14.37
The cube duplicated
at 50 frames
Scale the circle down.
Figure 14.38
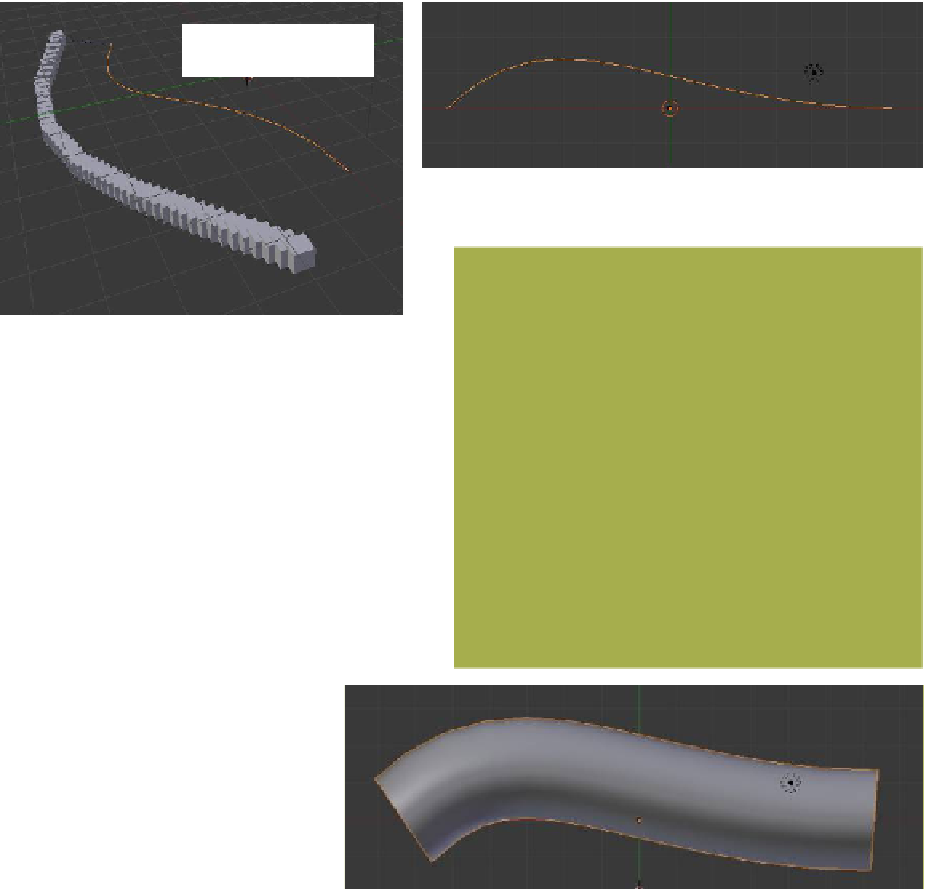
14.7 Extruding along Curves
A shape can be extruded along a curve to produce
a different shape. For example, start with the de-
fault Blender scene and delete the cube object.
Add a Bezier curve and scale it up along the
x
-
axis. For simplicity, put the window into top view
(number pad 7 - number pad 5). he curve may
be scaled and shaped in edit mode to produce a
shape for your extrusion to follow.
Deselect the curve and add a Bezier or
NURBS circle; the circle may be shaped in edit
mode to produce a cross section
shape for your extrusion. Scale the
circle way down (Figure 14.37). De-
select the circle and select the curve.
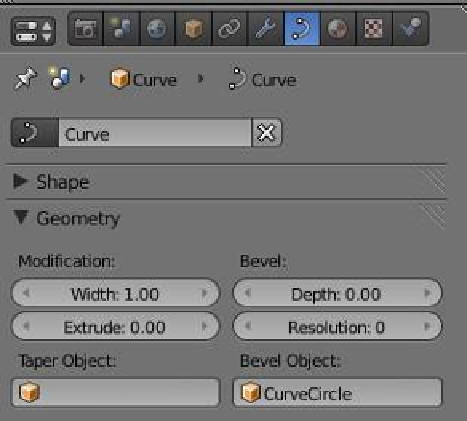
In the properties window - “Object
Data” button - “Geometry” tab, en-
ter “Curve Circle” in the “Bevel Ob-
ject” data panel and adjust the scale
as required (Figure 14.38).
14.8 The Follow Path Constraint
The follow path constraint causes an object in an animation to follow a path that has been
set as the target. This constraint is combined with the follow curve constraint that, when
set, causes the object to rotate and bank as it follows the path. The follow path constraint
can also be used to duplicate objects along a path and to extrude an object along a path. In
an animation, the motion of the object is set by inserting key frames (see Chapter 9 for a
refresher). When using the follow path constraint, the key frames are set in the properties