Graphics Programs Reference
In-Depth Information
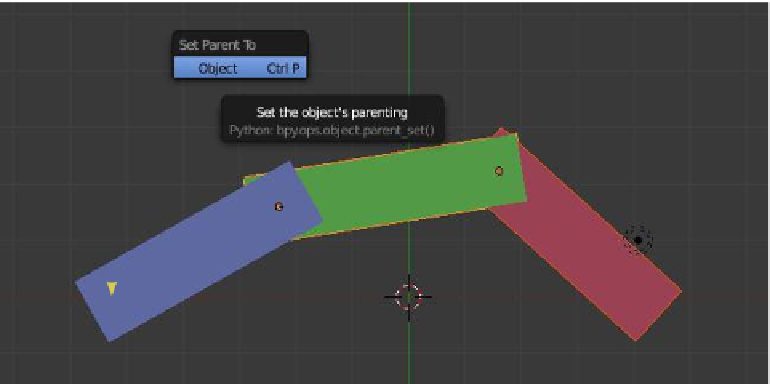
Figure 14.4
The red cube rotates
alone about this
center point.
The blue, green,
and red cubes
rotate about the
center here.
The green and red
cubes rotate about
this center.
14.2 Introduction to Constraints
Constraints are object features that define spatial relationships between objects. They are
the standard method for controlling characters among all 3D animation packages that still
implement a more traditional approach to digital character animation. In Blender, con-
straints can be associated with objects; note, however, that not all constraints work with all
objects. Constraints are associated with an object by selecting the object in the 3D window
then clicking on “Add Constraint” in the properties window - “Object Constraints” tab
and selecting the constraint
from the drop down menu
that displays (Figure 14.5). In
many cases a control object
will be required to make the
constraint function. There are
control values to be inserted to
regulate the function.
The following pages in this
chapter contain a brief descrip-
tion of constraint functions.
Most constraints are self ex-
planatory, therefore a detailed
explanation will only be given
for a few common constraints
or where it is not self evident.
Figure 14.5
Click “Add Constraint” to
display the constraint list.
Click to select a
constraint.
14.2.1 Constraint Stacks
It should be noted that in some
cases it is appropriate to apply