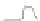Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
GREENLAND
U.S.
(Alaska)
60
°
CANADA
40
°
40
°
UNITED STATES
ATLANTIC
BERMUDA
OCEAN
BAHAMAS
MEXICO
Tropic of Cancer
CUBA
DOMINICAN
REPUBLIC
20
°
20
°
20
°
JAMAICA
U.S.
(Hawaii)
BELIZE
HONDURAS
NICARAGUA
HAITI
PUERTO
RICO
PACIFIC
GUATEMALA
EL SALVADOR
COSTA RICA
PANAMA
BARBADOS
TRINIDAD & TOBAGO
VENEZUELA
OCEAN
SURINAME
FRENCH GUIANA
COLOMBIA
GUYANA
0
°
Equator
ECUADOR
BRAZIL
PERU
BOLIVIA
20
°
20
°
20
°
Tropic of Capricorn
PARAGUAY
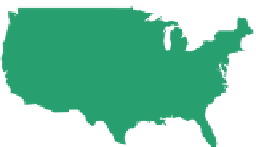
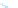
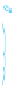
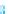
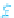
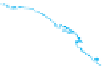
HUMAN DEVELOPMENT
INDEX, 2010
URUGUAY
CHILE
ARGENTINA
Very high human development
40
°
40
°
40
°
40
°
High human development
Medium human development
160
°
140
°
120
°
80
°
60
°
40
°
Low human development
60
°
60
°
60
°
60
°
SOUTHERN
OCEAN
No data
0
1000
2000
3000 Kilometers
0
1000
2000 Miles
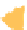
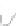
Figure 10.7
Human Development Index, 2010.
Data from:
http://hdr.undp.org/en/media/HDR_2010_
EN_Table1_reprint.pdf
Once peripheral countries owe money to the IMF,
the World Bank, and private banks and lending institu-
tions, they need to repay their debts. Spending a large
part of the country's budget on debt repayment makes
it diffi cult for a country to invest in more development
projects. For many countries the cost of servicing their
debts (that is, the cost of repayments plus interest)
exceeds revenues from the export of goods and services
(Fig. 10.8). Meanwhile, in many countries, the returns
on development projects have been much lower than