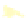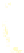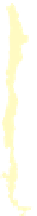Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
GREENLAND
U.S.
(Alaska)
60°
CANADA
40°
40°
UNITED STATES
ATLANTIC
BERMUDA
OCEAN
BAHAMAS
CUBA
MEXICO
Tropic of Cancer
DOMINICAN
REPUBLIC
PUERTO
RICO
20°
20°
20°
JAMAICA
U.S.
(Hawaii)
BELIZE
HAITI
HONDURAS
NICARAGUA
GUATEMALA
BARBADOS
TRINIDAD & TOBAGO
EL SALVADOR
PACIFIC
COSTA RICA
PANAMA
VENEZUELA
COLOMBIA
SURINAME
FRENCH GUIANA
GUYANA
Equator
0°
ECUADOR
OCEAN
PERU
BRAZIL
BOLIVIA
20°
20°
20°
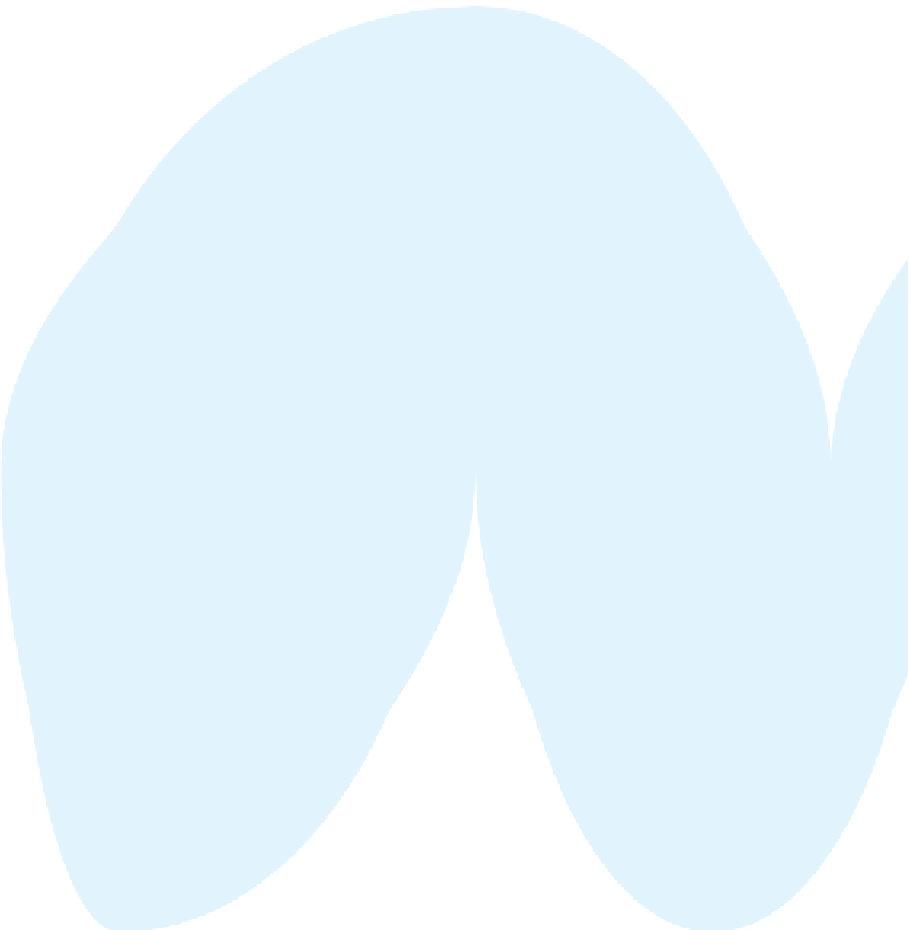
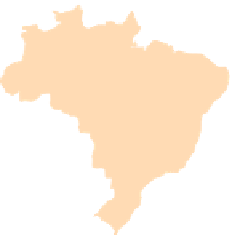
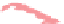
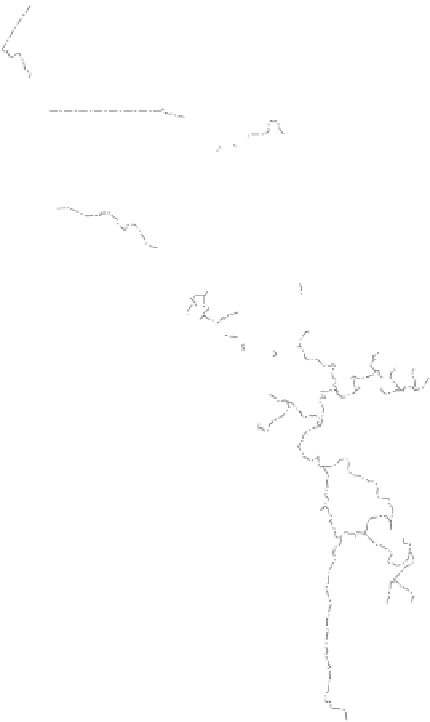
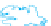
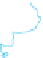
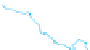
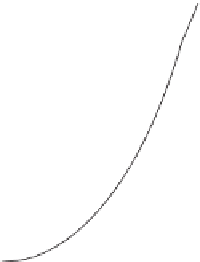
WORLD - PERCENTAGE
OF ARABLE LAND
PARAGUAY
Tropic of Capricorn
Very High
Over 35%
ARGENTINA
CHILE
URUGUAY
High
21-35%
40°
40°
40°
40°
Adequate
11-20%
Low
5-10%
Very low
Below 5%
160°
140°
120°
80°
60°
40°
60°
60°
60°
60°
SOUTHERN
OCEAN
Data not available
2000
0
1000
3000 Kilometers
0
1000
2000 Miles
Figure 1.4
Percent of Land That Is Arable (Farmable), 2008.
Data from
: United Nations Food and
Agriculture Organization, 2011.
As I drove through the contrasting landscapes, I continued to question
whether it would be better for the fertile highlands to carry food crops that could
be consumed by the people in Kenya. I drove to the tea processing center and
talked to the manager, a member of the Kikuyu ethnic group, and asked him my
question. He said that his country needed foreign income and that apart from
tourism, exporting coffee and tea was the main opportunity for foreign income.
As part of an increasingly globalized economy, Kenya suffers from the com-
plexities of globalization. With foreign corporations owning Kenya's best lands, a
globalized economy that thrives on foreign income, tiny farms that are unproduc-
tive, and a gendered legal system that disenfranchises the agricultural labor force
and disempowers the caregivers of the country's children, Kenya has multiple fac-
tors contributing to poverty and malnutrition in the country. In addition to these
structural concerns, Kenyan agro-pastoralists, especially in the northeast, have