Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
60.0
30.0
25.6
24.2
50.0
25.0
20.1
40.0
20.0
Execution time
Encoding speed
30.0
15.0
13.6
20.0
10.0
10.0
5.0
3.3
0.0
0.0
CPU
transfer
CPU
transfer
DMAC
transfer
DTU
transfer
w/o list
DTU
transfer
with list
1 CPU
1 CPU + 1FE-GA
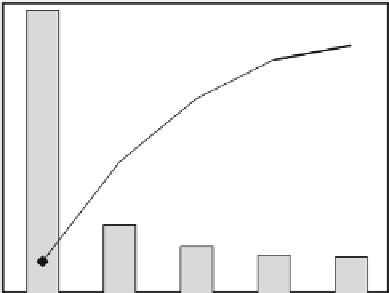
Fig. 6.6
Performance improvements with various data transfer methods
The evaluation results indicate that the efficient use of accelerators for process
executions and DTUs for data transfer plays an active role in improving performance.
Performance with the DTU was better than that with the DMAC because twice as
many transactions of the interconnection bus are required with the DMAC than with
the DTU, and this bus is slower than the CPU internal bus connected directly to the
URAM and DTU. The beneficial effect of the DTU transfer lists is due to a reduction
in the number of DTU register setups for multiple transfers to the banks of the local
memory in the FE-GA. Since the FE-GA has multiple banks of memory, divided data
are placed in different banks, and transfers are done multiple times. As a result, the
number of DTU operations is reduced by utilizing transfer lists.
6.1.6
Performance Evaluation in Parallelized Processing
We measured the performance of AAC encoding on the evaluated chip. The evalu-
ation included the execution time and average power consumed in the encoding.
The encoding process was mapped to the four processor cores as outlined in Fig.
6.7
.
For simple implementation of parallel processes, two streams of encoding were
individually assigned to a pair of one CPU and one FE-GA. However, processing
tasks of the encoding on both a CPU and an FE-GA in parallel will be achieved by
utilizing inter-frame parallelism.
The evaluation was done under the conditions listed in Table
6.2
. The perfor-
mance was measured with double input streams of music-2. In other words, the





























Search WWH ::

Custom Search