Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
the repulsive solvophobic interaction should be a major driving force
for the superparticles to adopt a spherical shape, in which they have
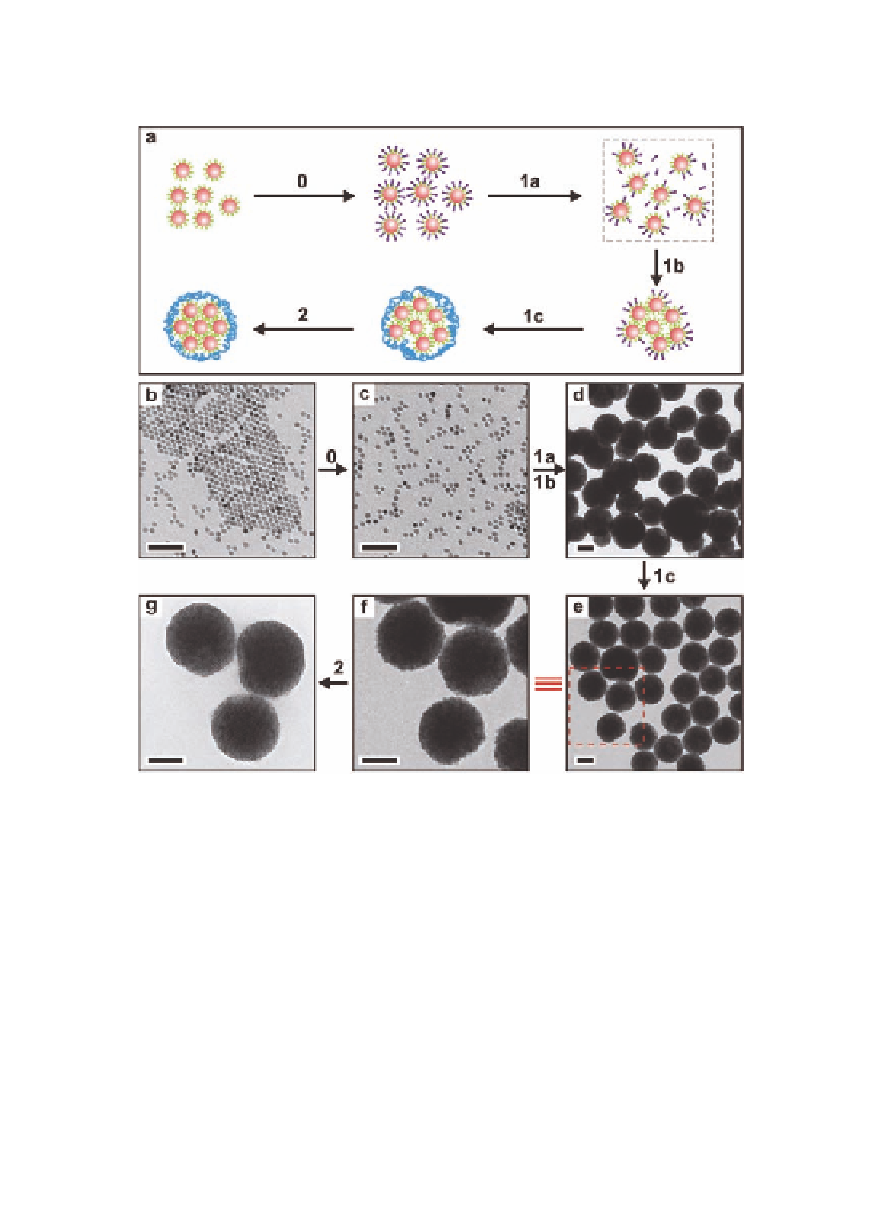
Figure 13.9
(a) A schematic representation of the proposed formation
mechanism of supercrystalline superparticles. (b) TEM
image of oleic acid functionalized Fe
O
nanocrystals, (c)
3
4
−
nanocrystal micelles, (d) superparticles made
without PVP at room temperature, and (e) superparticles
capped with PVP at room temperature. (f ) An enlarged
image of the inset in (e). (g) A TEM image of superparticles
after annealing at 80
DTAB
Fe
O
3
4
°
C for 6 h. Scale bars: 50 nm (b and
c), 100 nm (d-g). The synthesis stages are (0) synthesis
of nanocrystal micelles as precursors; (1) aggregation
−
1a: controlled induction of solvophobic interactions via
nanocrystal micelles decomposition, 1b: aggregation of
Fe
nanocrystals, and 1c: passivation with PVP; and (2)
crystallization. From Ref. [1] with permission.
O
3
4
Search WWH ::

Custom Search