Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
there may be some possibility for a special kind of microcomponents
with small contacts, which have the characteristic of larger surface-
to-volume ratios, as the corrosion process likely depends on the
exposed surface area.
12.3.3
Microscale 3D Self-Assembly
Compared to conventional 2D microscale self-assembly, 3D self-
assembly processes are more challenging, as they set higher
requirements for both the components, the substrate and the self-
assembly mechanisms.
In microdomains, capillary force dominates over gravity, and
has been exploited to construct 3D self-assembled structures. Our
group has demonstrated some work of achieving 3D microscale
self-assembly by applying capillary force provided by hydrophobic
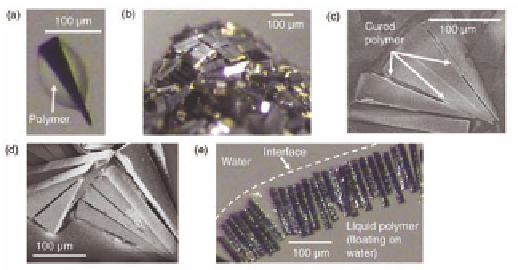
and hydrophilic interactions [12]. As shown in Fig. 12.17, a cross-
linkable liquid polymer was used as an intermediate to promote the
binding of microscale silicon parts into 3D structures. In the review,
we also systematically quantified the effect of various parameters
that affect the polymer-deposition process, such as the surface
energy of template regions, polymer concentration, and size of the
template regions.
Figure 12.17
Self-assembly of triangular, microfabricated silicon parts.
(a) One unassembled part. (b) Large collection of microscale
components due to deposited polymer. (c) Self-assembly of
a small number of parts into the desired configuration. (d)
Self-assembly from a different experiment. (e) Collection of
stacked triangular parts floating near the edge of a polymer
droplet on a water surface. Reprinted with permission from
Ref. [12]. Copyright 2006 IEEE.


Search WWH ::

Custom Search