Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
n
-octadecylphosphonic acid (ODPA), and phenylphosphonic acid
(PhPA), were utilized for supportive experiments investigating the
role of
π−π
stacking and hydrogen bonding in the self-assembly
process [3].
The effect of solvent on PYPA assembly was studied by spin-
coating PYPA from solutions of methanol, ethanol, 1-propanol,
tetrahydrofuran (THF), and
N,N
-dimethylformamide (DMF) on Si\
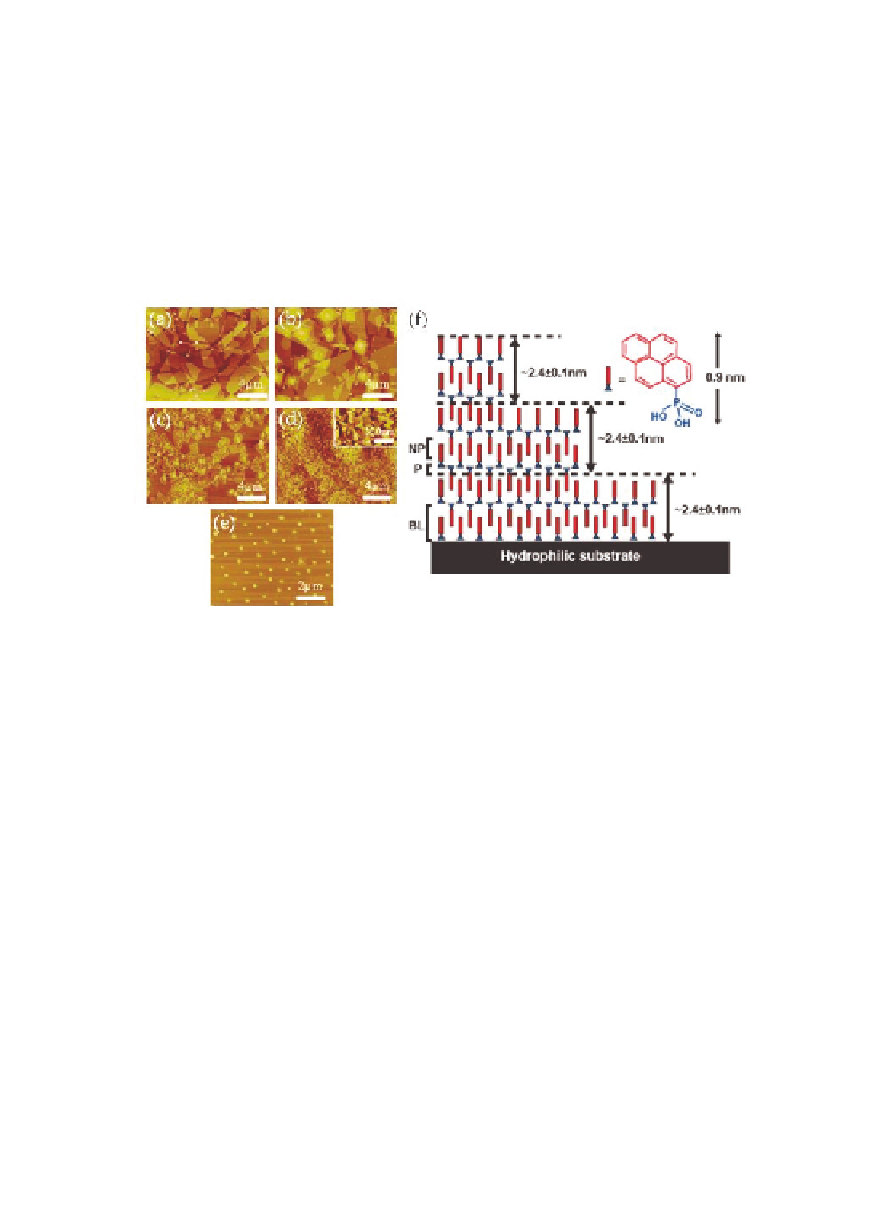
substrates. Figure 12.3 displays AFM images of the laminate
structures obtained after evaporation of the solvents.
SiO
2
Figure 12.3
AFM
deposited from
solutions of (a) methanol, (b) ethanol, (c) 1-propanol, (d)
tetrahydrofuran, and (e)
micrographs
of
PYPA
on
SiO
2
-dimethylformamide (1 mM). (f )
Schematic of proposed internal laminate structure of PYPA
with alternating polar phosphonic acid and nonpolar pyrene
headgroups forming interdigitated bilayers. Reprinted with
permission from Ref. [3]. Copyright 2006 American Chemical
Society.
N,N
Solutions utilizing short alkyl chain protic solvents resulted
in the formation of robust laminate structures of square-shaped,
micrometer-size crystals randomly distributed on the surface.
Stacked upon each other, they form a continuous polycrystalline film.
The PYPA crystals developed at the air/solvent interface, and, owing
to their slide planes being perpendicular to the lamellar plane, they
assembled on the substrate via sliding down on already deposited
crystals. AFM measurements revealed a multilamellar structure
with defined step heights (Fig. 12.3). A proposed internal laminate
structure is schematically shown in Fig. 12.3. Polar (P) regions
Search WWH ::

Custom Search