Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
completely passivates the grooves of the surface in such a way as to
hold the CR molecules proximal both end to end and side to side.
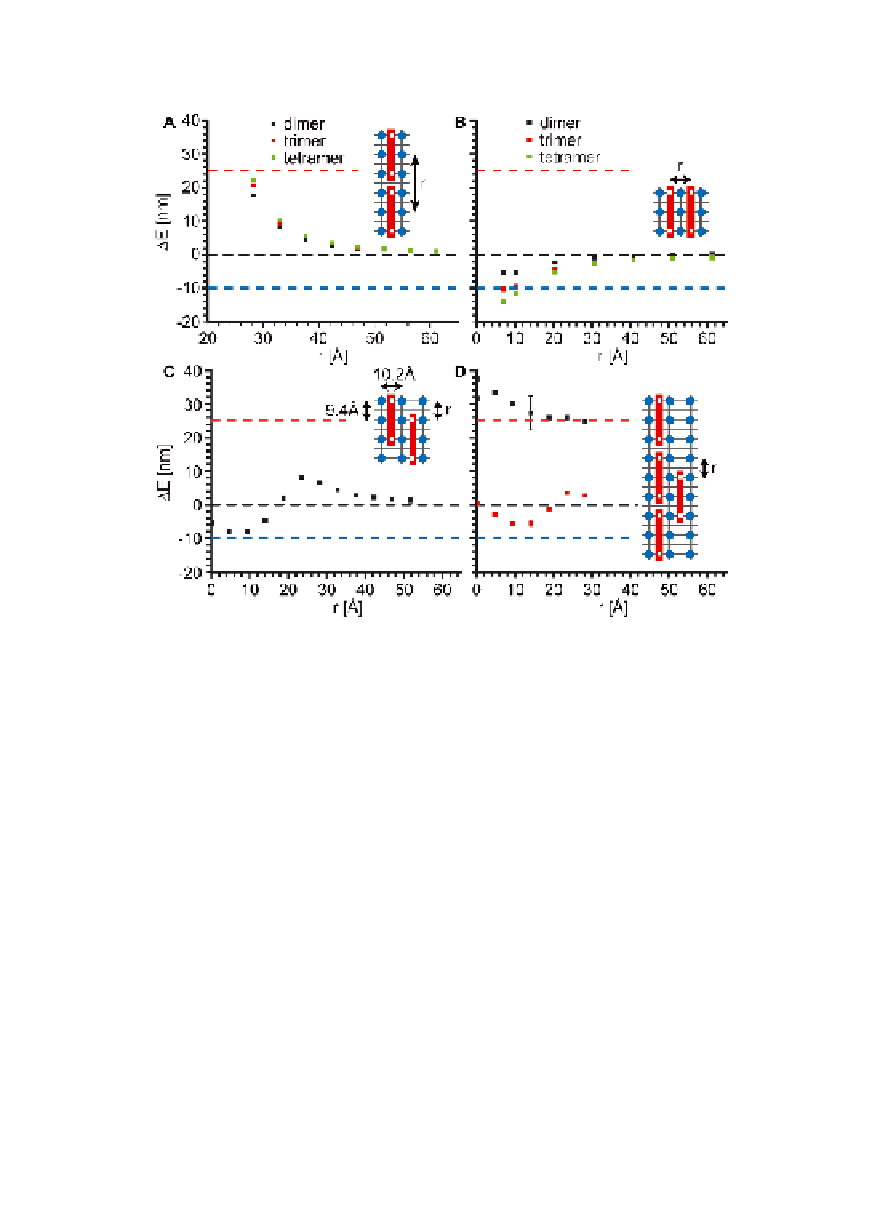
Figure 1.12
Calculated ZINDO/S exciton coupling energy (Δ
E
) as a
function of center-to-center distance,
r
, for CR molecules
(
A
) aligned end to end as J-aggregates and (
B
) aligned side
to side as H-aggregates, (
) as a function of registry within
a CR H-aggregate dimer, and (
C
) the registry of a monomer
relative to a J-aggregate CR trimer. The error bar indicates
the maximum calculated variability in Δ
D
. The red and
blue dashed horizontal lines represent the experimentally
observed red- and blue-shifts for CR bound to KLVFFAL
nanotubes. The cartoon insets display the separation (
E
)
between CR molecules, with β-sheets separated by 10.2
Å forming the laminate grooves and H-bonded peptides
separated by 4.7 Å. Similar to the surfaces shown in Figs.
1.10D and 1.11, the blue circles indicate positions of
N-terminal lysines and the red blocks are CR molecules with
the position of the sulfates indicated by white squares. The
anti-parallel registry within the
r
β
-sheet places the lysines
at the corners of a 9.4 x 10.2 Å rectangle. Δ
is the energy
splitting arising from exciton coupling and is the difference
in transition frequency between the aggregate and monomer
[92].
E
Search WWH ::

Custom Search