Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
-
O
3
S
SO
3
-
N
N
N
N
NH
2
H
2
N
Congo Red
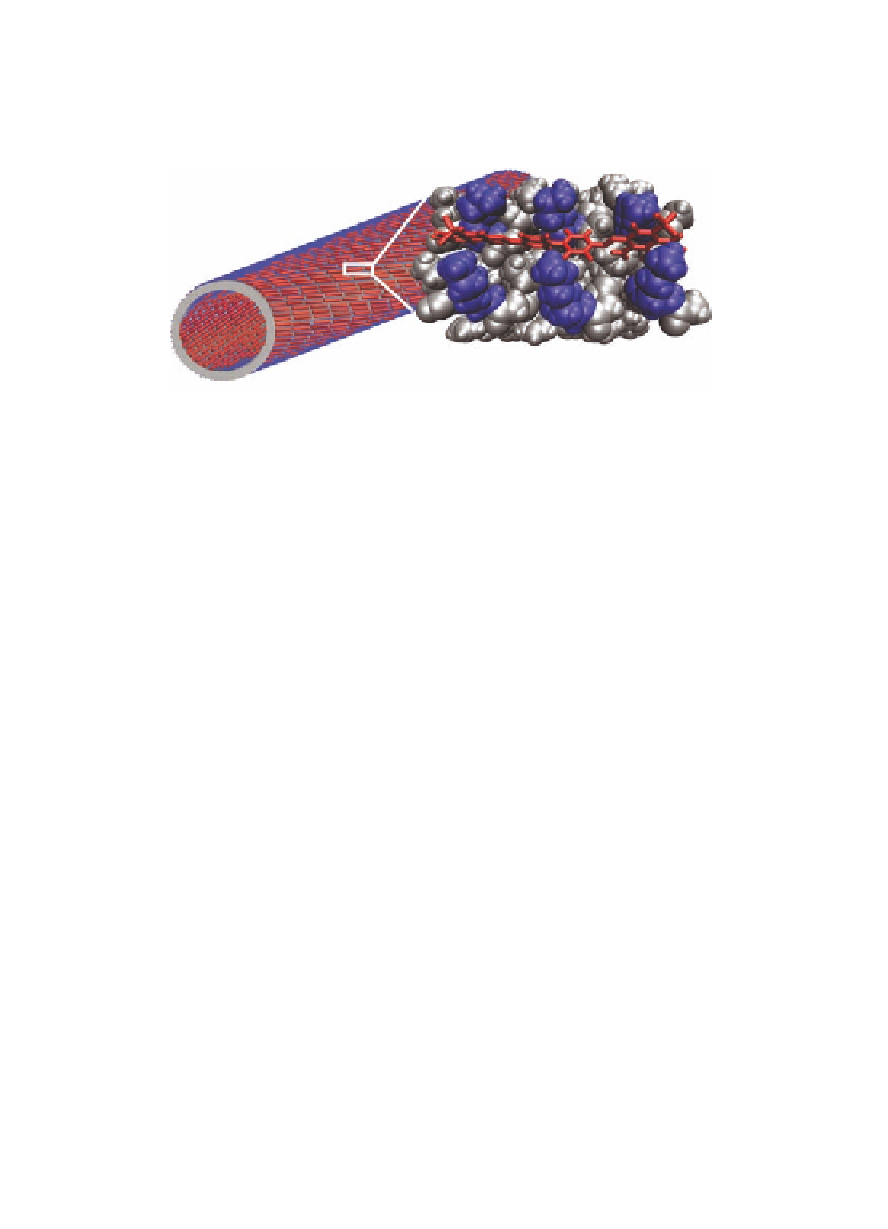
Figure 1.11
Model of the Congo red, KLVFFAL laminate-groove binding
site. The residues in close proximity to CR are shown in
space-filling format as follows: hydrophobic residues (gray),
lysines (blue), Congo red (red, displayed in stick format)
[92].
Simulations of the energy splitting arising from exciton coupling
(Δ
) as a function of the distance between CR molecules were used to
model the characteristic spectroscopic signatures of the assemblies
(Fig. 1.12). The calculated shift in
E
increased as the center-to-
center distance decreased, but even the closest spacing expected
for only two CR molecules bound to the cross-β laminate grooves
did not match the experimentally observed shifts (horizontal
red- and blue-dashed lines in Fig. 1.12A). However, the coupling
strength (Δ
λ
max
) for trimer and tetramer CR systems was sufficient
to explain the experimental data and accurately reproduce the CR
aggregate arranged on the cross-β termini surface. In addition,
fixing CR molecules to neighboring laminates (Fig. 1.12C) revealed
the orientation dependence of the exciton coupling, suggesting that
the pure H-character becomes more J-like as the center-to-center
distance between the molecules is increased. Such organization
positions CR molecules well within the range of distance-dependent
exciton coupling for both J-aggregates (<45 Å, Fig. 1.12A) and
H-aggregates (<30 Å, Fig. 1.12B) and provides a clear structural
explanation for the well-known histochemical signature consistent
with bound CR arrangements observed in diverse amyloid [100].
And maybe most importantly for this discussion, the CR association
E

























































































































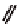




























Search WWH ::

Custom Search