Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
can be imagined that such associations could stabilize or destabilize
certain crystalline polymorphs and/or can passivate the surfaces
for construction of even higher order supramolecular assemblies.
For example, in the case of the metal bound assemblies, one surface
creates a two-dimensional organized array of metals at well-defined
intervals along the entire solvent-accessible interface [81].
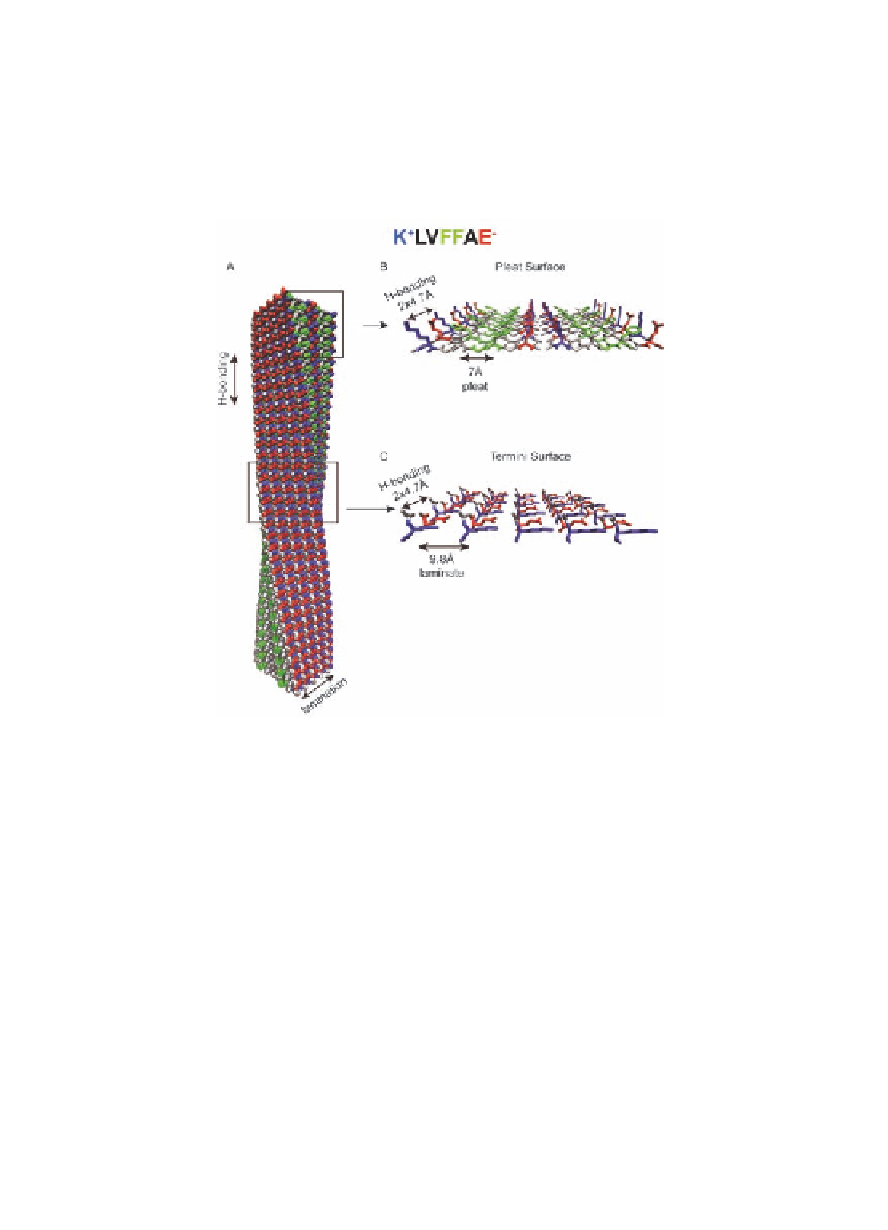
Figure 1.9
(
β
fiber consistent with dimensions from electron microscopy
(Fig. 1.3A) [23]. H-bonding between
A
) Structural model of the KLVFFAE 5 nm x 5 nm cross-
β
-strands runs along
β
the fiber long axis and
-sheet stacking (lamination) is
perpendicular to the H-bond axis. H-bonding places the
peptide repeat at 4.7 Å (
) Polar pleat surface, as highlighted
in Fig. 1.3B, is composed of lysine (blue), valine (gray),
phenylalanine (green), and glutamic acid (red) residues. The
remaining residues are displayed on the opposite
B
β
-sheet
face. The pleat channels are defined by the exposed amino
acid side chains, which are spaced every 7 Å. As illustrated
in Fig. 1.8, the pleat surfaces are hidden when the number
of laminates increases and helically coil into tubes. (
) The
termini surface is composed of peptide termini, lysine (blue)
and glutamic acid (red) residues, and capping groups (gray).
The
C
-sheets are stacked on top of each other and separated
by 9.8 Å.
β
Search WWH ::

Custom Search