Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
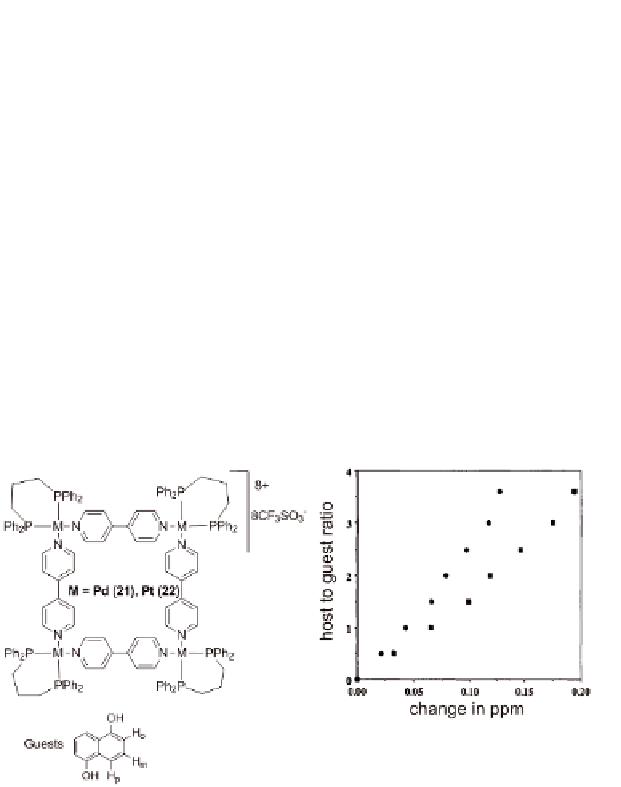
methanol to give corresponding inclusion complexes [74]. For
example, a significant upfield shift of
∼
0.11 ppm for
ortho
protons and
0.2 ppm for
protons of 1,5-dihydroxynaphthalene was observed
as a function of concentration in the
meta
1
(see
Fig. 10.4). Thus, the rational design of efficient hosts for molecular
recognition involves the introduction of specific recognition sites
into the assembly. Stang
H NMR titration with
21
have designed molecular squares with
Lewis base receptor sites, which show a variety of metal-binding
capability and geometrical predictability. X-ray crystallography of
the Lewis acid/base host
et al.
−
with phenazine
provided new insight into molecular recognition design [75]. There
are several interesting structural features evident for this complex.
The overall geometry of the perimeter for this complex is almost
planar with the guest phenazine oriented nearly orthogonal to the
Pt
guest molecular square
23
−
2+
−
Pt
Pt plane.
∑
Figure 10.4
Plot of change in chemical shifts of the
)
protons of guest molecule as a function of concentration of
host
ortho
(
) and
meta
(
21
. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [74].
π
The
-complexed silver atoms are located in a pseudo
trans
−
2+
−
arrangement with respect to the Pt
-
symmetric relationship. Interestingly, the acetylene moieties in the
backbone of the molecular square
Pt
Pt plane, resulting in a C
i
23
interact with two equivalents
of silver triflate to give a host
, with considerable
stability in solution. Further, the metallacylic square
−
guest complex,
24
serves as a
receptor to bind Lewis basic guests with the appropriate size being
achieved through the coordination of silver cations via “
24
π
-tweezer

Search WWH ::

Custom Search