Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
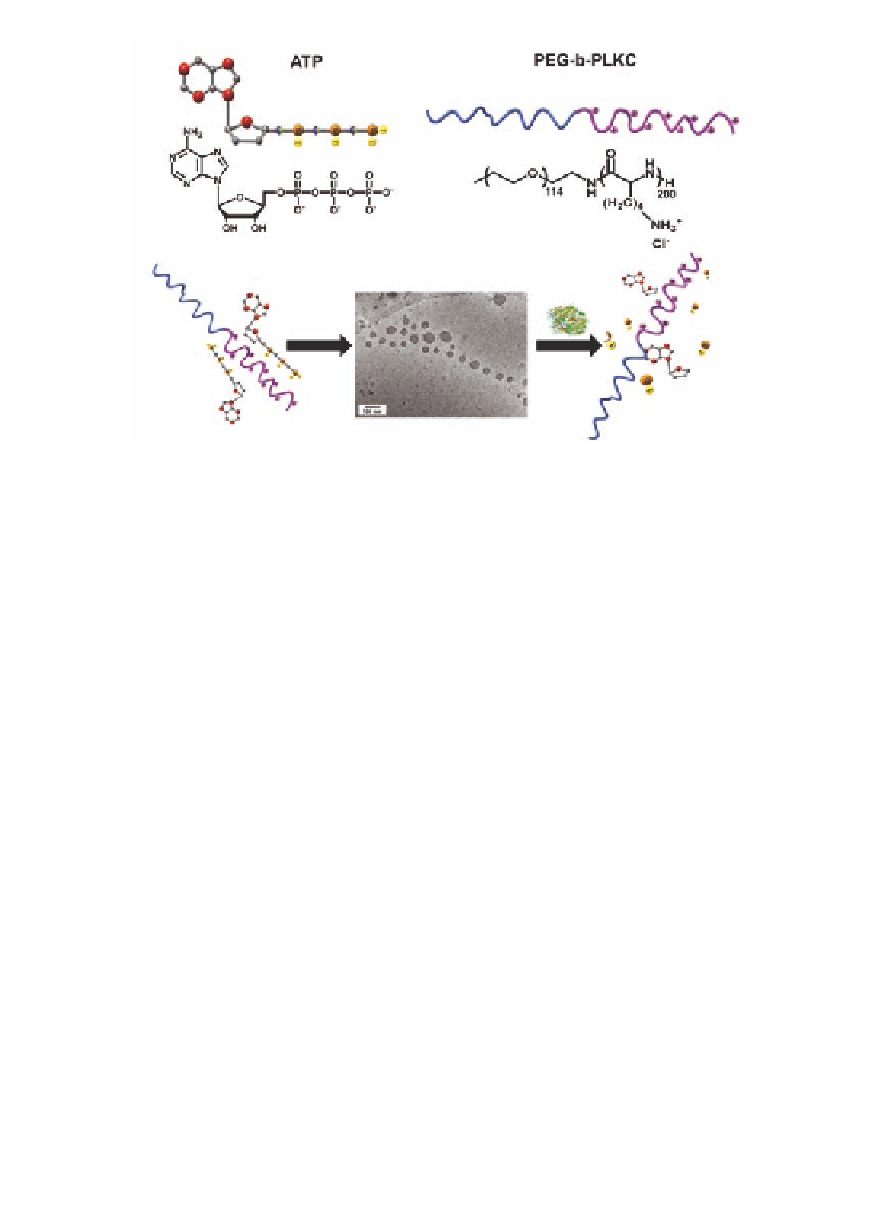
Figure 6.9
Enzyme-responsive supra-amphiphiles. Reproduced with
permission of Ref. [36]. Copyright 2010, Wiley-VCH Verlag
GmbH & Co. KGaA.
6.4.3
Responsive Surface
The property of the responsive supra-amphiphile can also be
introduced to the surfaces, resulting in functional surfaces. For
example, the rotaxane-like supra-amphiphile can also be transferred
to surfaces, displaying different properties as those in aqueous
solution. For example, we can transfer a rotaxane-type supra-
amphiphile onto a rough gold substrate using self-assembled
monolayers (SAMs), and therefore control the wettability in response
to photo-stimuli [37]. For this purpose, an azobenzene-containing
building block with a mercapto group at the end preassembled with
α
-CD in water based on the interaction between azobenzene and
α
-CD, forming a supra-amphiphile. This supra-amphiphile can form
a mixed SAM with n-butylthiol on a gold substrate. Before UV-light
irradiation,
α
-CD stays on the top of the surface, and the SAM displays
hydrophilic properties. After UV-light irradiation,
-CD moves down
onto the alkyl chain and the SAMs become more hydrophobic. When
irradiated by visible light, the
α
-CD can move up, making the surface
more hydrophilic once again. A change of nearly 50
α
of the surface
contact angle with a water droplet is shown before and after UV-
°
Search WWH ::

Custom Search