Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
phenomena are shown in Fig. 5.4b. The larger
values observed for
the folded structures arise because the bay protons (Hb) experience
a larger ring current than the outer protons (Ha) when the two
aromatic rings are
∆
d
π
∆
d
value as a reliable
indicator of folded structures versus nonfolded structures. For free
monomer (
-stacked. This makes the
1A
),
∆
d
is 0.061 ppm, whereas the
∆
d
values (Fig. 5.5) for
folded dimer (
2A
), trimer (
3A
), and tetramer (
4A
) are 0.26, 0.33,
and 0.38 ppm, respectively.
8.6
Unfolded or Free
Self-Organizing
8.4
Folded
dimer
8.2
Folded
trimer
8.0
Folded
tetramer
7.8
7.6
7.4
10
-5
10
-4
10
-3
10
-2
10
-1
Concentration [A
o
]
Figure 5.5
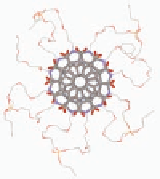
Folded hexamer (
) side view (top left) and end view
(top middle) is contrasted to a self-assembled hexamer
(
6
) viewed from the end showing
unconnected TEG chains. Bottom: Plot of the observed
chemical shifts Ha (open) and Hb (filled) of monomer
1A:1A:1A:1A:1A:1A
1A
(circles), dimer
2A
(diamonds), trimer
3A
(triangles), and
tetramer
(squares) as a function of the initial molar
concentration of each species. The chemical shift separation
between Ha and Hb is very small for free monomer below
self-assembly critical concentration (
4A
C
= 1 mM) and is very
C
large for the folded oligomers
2A
−
4A
; this effect is caused by
π
the ring current of the
-stacked perylene neighbors.


















































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search