Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
quartet interconversion by controlled sequential addition and
removal of the cation. By addition of K
+
, the ribbon-like aggregate
of LG in chloroform is transformed into the octameric complex.
Subsequent addition of cryptand [2.2.2], which offers an efficient
complexation of K
+
+
⊂
2.2.2] and reverts the
LG to the ribbon form. Upon protonation of one of the bridgehead
nitrogen atoms of the cryptate, leading to the formation of [H
, yields the cryptate [K
+
⊂
can be released and is available again for LG
complexation (Fig. 4.16) [32a].
2.2.2], the bound K
+
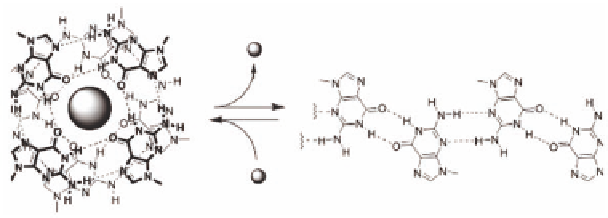
Figure 4.16
The tunable interconversion between two highly ordered
supramolecular motifs (K
+
-templated G-quartet column
and G-ribbon) of a lipophilic guanosine derivative fueled by
cation complexation and release.
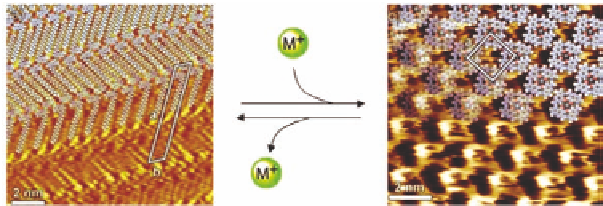
The same process of switching between the ribbon and the
G-quartet-based form can be observed not only in solution but
also on surfaces in the case of derivatives
. By scanning tunneling
microscopy it is possible to actually watch the ribbons on a graphite
surface (Fig. 4.17, left) to cluster in a quartet pattern after the
2
Figure 4.17
STM images of the reversible switching between ribbon-like
(left) and G-quartet-based (right) assemblies of a lipophilic
guanine derivative on graphite.


Search WWH ::

Custom Search