Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
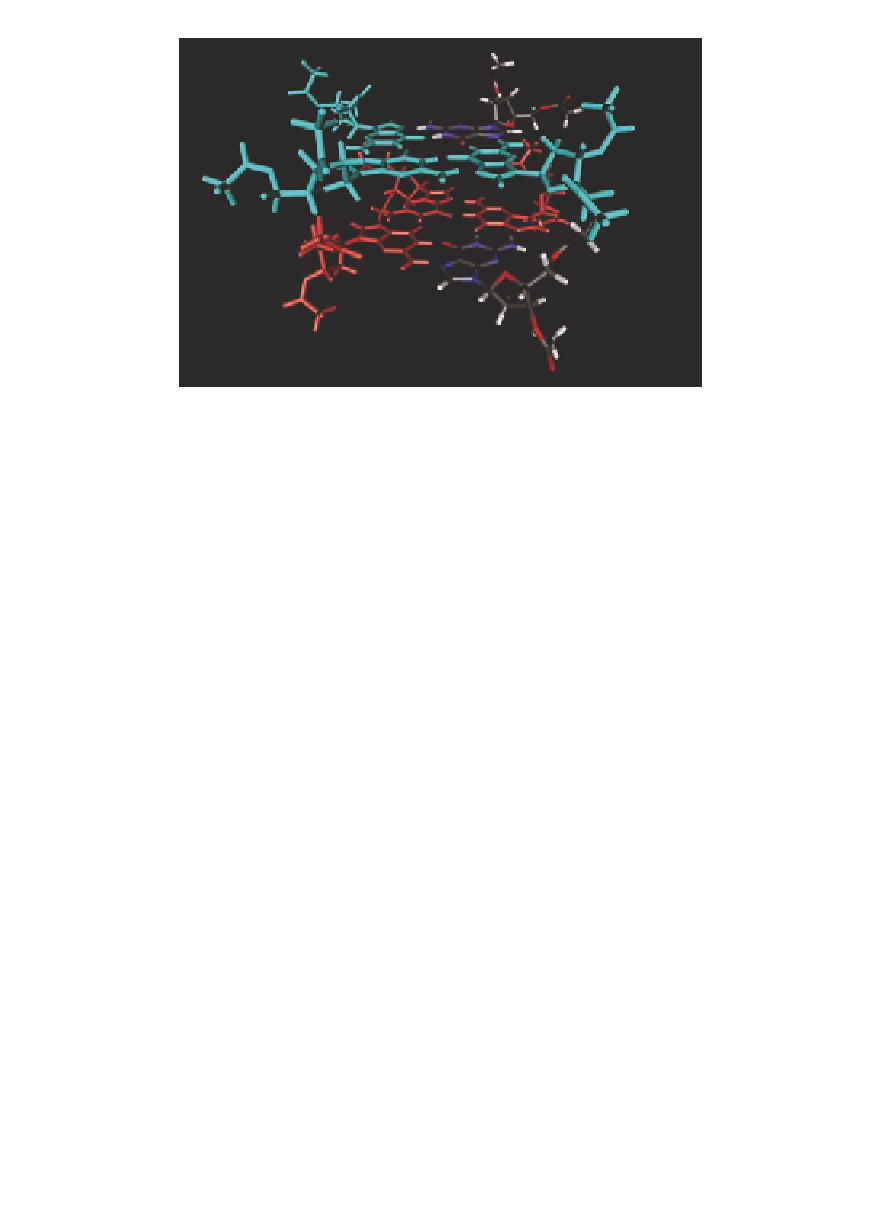
Figure 4.7
The structure of the LG
K
+
octameric complex (the metal ion
at the center is not shown for clarity): an all-
8
.
G-quartet
(three molecules are colored in light blue) with its head side
stacks on the tail side of an all-
anti
syn
G-quartet (three molecules
are colored in red).
This stereoselectivity and stereoregularity for the octameric
noncovalent assembly is striking. Davis also succeeded in
obtaining good crystals of the complex of a similar derivative (5
′
-
t-butyldimethylsilyl-2
-isopropylideneguanosine [14]: the X-ray
structure confirmed that, in the octamer, the two G-quartets are in a
head-to-tail arrangement, and that the conformation of guanosine is
all
′
,3
′
in the other. Furthermore, the picrate
anion is not passive, as it contributes to keep together the complex
structure by means of hydrogen bonds with the exocyclic NHs of two
different quartets. The binding contribution of the picrate anion was
also evident from an ESI-MS study [15].
syn
in a quartet and all
anti
-
polymer by NMR and small-angle neutron scattering (SANS)
spectroscopy [16]. Also, this assembly is stable over a temperature
range of approximately 100°C.
Subsequently, we solved the solution structure of the
pseudo
1
H-NMR spectra of the polymeric
aggregate are relatively simple, showing three sets of signals (not
interconverting on the NMR chemical shift time scale) in a 1:1:1
ratio. Each set corresponds to guanosine monomers with a different
conformation (one
anti
rotamer, and two different
syn
conformers,
8
.
+
syn1
and
syn2
). Like the
C
4
-symmetric LG
K
octamer, each G-quartet
within the (LG
4
.
K
+
)
polymer is homogeneous in terms of its rotamer
n
Search WWH ::

Custom Search