HTML and CSS Reference
In-Depth Information
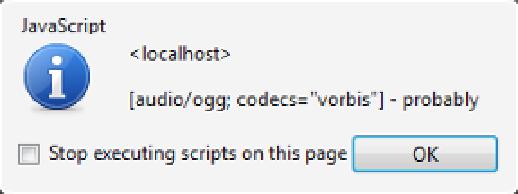
Try running the application using Opera and the alert should look like Figure
8-15
.
Figure 8-15.
The canPlayType() results for audio/ogg; codecs' ”vorbis”
“Probably” is as good as you'll get, with the
canPlayType()
method anyway; you don't ever get a “yes”. The
possible responses are illustrated in Table
8-2
.
Table 8-2.
canPlayType() method responses
Codec
Container Supported
Container Not Supported
Undefined
“maybe”
Blank
Supported
“probably”
Blank
Not Supported
Blank
Blank
Understanding Video Formats
As I said at the beginning of the chapter, the
video
element works just like the
audio
element so everything you
have learned so far also applies to video.
Reviewing Browser Support
A video file usually contains both audio and video so all of the audio types and codecs that I covered earlier
still apply. In addition, the video portion can be encoded in various ways. Fortunately, the industry seems to be
narrowing down to three primary formats:
•
MP4 - (*.mp4) using H.264 video encoding and MP3 audio encoding
•
WebM - (*.webm) using VP8 video encoding and Vorbis audio encoding
•
Ogg - (*.ogv) using Theora video encoding and Vorbis audio encoding
Table
8-3
lists the formats that are supported by the major browsers
Table 8-3.
Video/Audio codec support
Browser
MP4
WebM
Ogg
IE 9
Yes
No
No
Firefox 4
No
Yes
Yes
Chrome 6
Yes
Yes
Yes
Safari 5
Yes
No
No
Opera 10.6
No
Yes
Yes