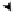Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
CDE I
CDE III
CDE II
*
*
AT
CC
A
G
T
G
C
T
A
G
T
T
T
T
TT
G
T
T
T
C C
G
A A
G
A
T
G
T
A
A
A
A
123456789 0
CG
TA
CG
A
G
T
CG
T A
G
T A
C
T A
CG
A
C
T A
1
CG
T
C
T
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
AA
G
A
GGG
T
ACG ACGAG
T
AGTACTCGTCGT A
C
C
G
GT CG
Modified nucleosome
Modified histone core
I
I
∗
E
C
II
M
i
c
r
o
t
u
b
u
l
e
D
D
C
E
I
CBF1
dimer
middle and
outer
kinetochore
proteins
CBF3
complex
C D
E I I I
*
FIGURE 1.49
Schematic representation in the inset of the simple centromere structure of the yeast kinetochore emphasizing the
positions of the two DNA-protein binding sites CDEI and CDEIII wrapped around the nucleosome core
comprised of the histone octamer. Indicated in a general way are the site binding proteins and the multiprotein
complex forming the kinetochore that binds to the microtubule responsible for separating the chromosome to the
appropriate daughter cell during cell division. Above this inset schematic are indicated the DNA sequences of
CDEI and CDEIII sites, with their centers of symmetry (asterisks) and symmetry elements (arrows) highlighted.
Below the sequence is indicated the binding site position number and below that the three possible mutants for
that position. All of the single base pair mutants of the CDEI and CDEIII sites were studied and the chromosome
loss rates resulting from each of the indicated mutants were determined (169). The logarithm of each chromoso-
mal loss rate is depicted by the length of each vertical line below each mutant position. Adapted from Hegeman,
J.H., Flieg, U.N. (1993). The Centromere of Budding Yeast.
BioEssays
15:451-460. With permission of Wiley-Liss,
Inc., a subsidiary of John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
CBF 3. As shown in the inset schematic, these complexes are in close proximity, since they
occur wrapped to form a modified centromere nucleosome found at the CEN sequence
location on each yeast chromosome. Both complexes subsequently participate in the self-
assembly of a complex multiprotein, multi-DNA sequence kinetochore on each chromo-
some. This large complex binds a long spindle microtubule in the cell, which then
correctly segregates the chromosome during cell division.
In a published report, the yeast chromosome 6 centromere DNA and dozens of CDEI and
CDEIII single base pair mutants were studied (169). Their relative chromosome loss rates
were measured during yeast cell division and the logarithm of those rates are presented in
Figure 1.49 as the vertical line lengths beneath each base mutant site position for both the
CDEI and CDEIII binding sites. In general, the more significantly the DNA mutant affects
interaction stability with the binding protein, the greater is the resulting chromosomal loss.
We reasoned that the mutants resulting in greater deformation of the original DNA
sequence by the protein would likely be those producing greater chromosome loss rates
through larger defects in kinetochore structure and energetics. Therefore, from the
sequences we calculated the change in absolute value of PD for all of the single base CDEI
and CDEIII mutants at all positions compared with the original wild-type sequence. We