Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
a
Antigen addition
Dispersed
carbon material
particle
First stage
incubation
Conjugate addition
b
Dispersed
carbon material
particle
HRP
HRP
HRP
Second stage
incubation
Substrates addition
c
Dispersed
carbon material
particle
I
−
e
−
I
2
H
2
O
2
HRP
H
2
O
Amperometric
detection
HRP
Unlabeled
antibody
Antigen
Conjugate
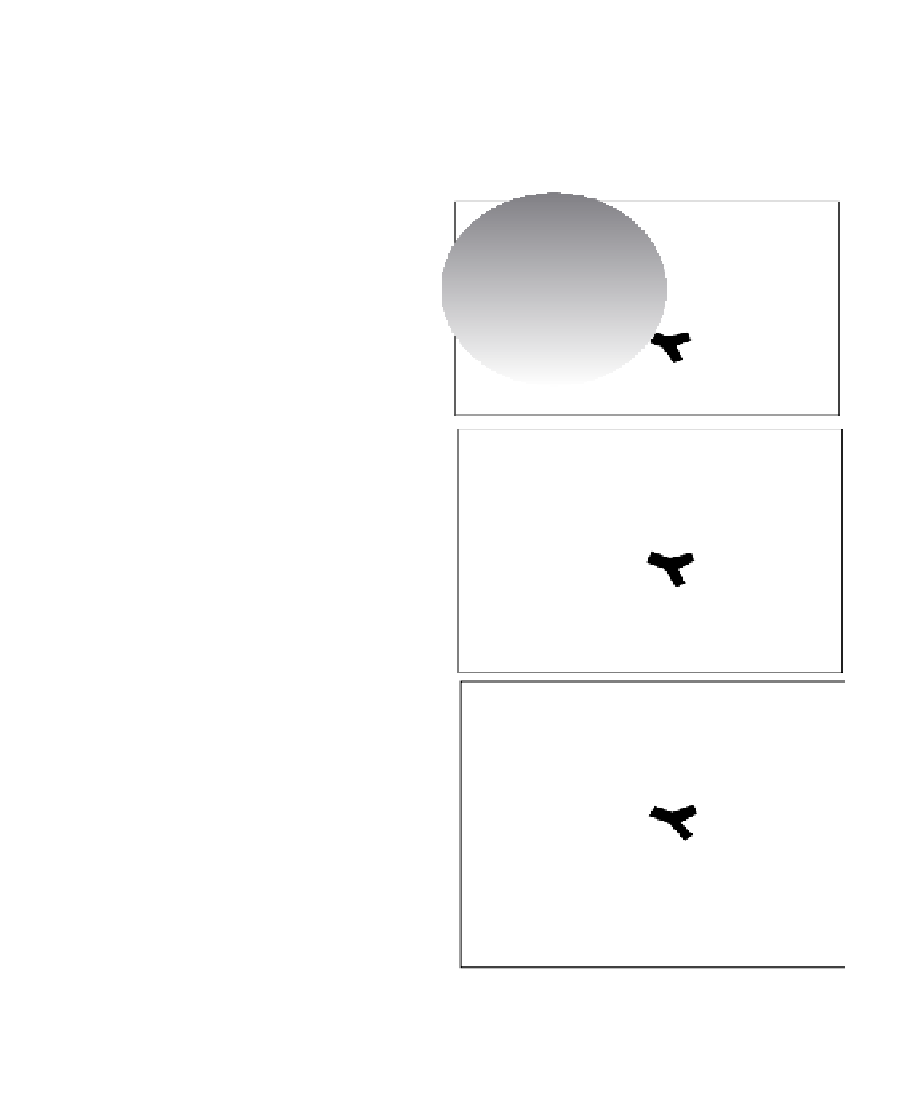
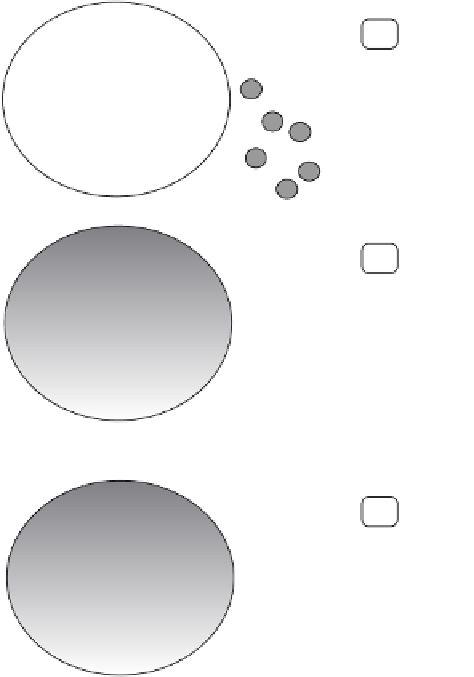
FIGURE 22.1
Sandwich scheme of immunochemical for carbon
particle immobilization.
Peroxidase labeled
antibody
Immobilized on
the dispersed
carbon material
was 20 mV/s. The results of these experiments allowed choosing the potentials of
working electrode for amperometric detection of products for HRP (iodine) and AP
(
-naphthol).
22.2.5.2 Selection of a Working Potentials
The working potential is the potential at which the working electrode is biased with respect
to the reference electrode. A suitable working potential has to be selected to achieve efficient
product formation during the enzymatic reaction of enzyme labels (AP for Hanta virus and
HRP for influenza viruses detection). Selection of a suitable working potential was performed
using cyclic voltammetry. For amperometric detection of AP activity, the background and
working voltammograms were obtained in the presence of 1 mM
-naphthyl phosphate
(substrate of AP) in a bicarbonate buffer solution pH 9.6 (Figure 22.2.)
The maximum oxidation current of
-naphthol as AP enzymatic reaction product is
observed at a potential of
100 mV (shown in Figure 22.2 as red arrow for peaks curves 1