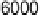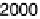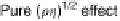Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
long fibrillike 2
m average width aggregate structures in aqueous buffered solution
(82,86,87). In these studies, following enzymatic polymerization by HRP, we measured the
continued presence in solution of long fibrillike monomer aggregates of DEDT.
The DEDT monomer self-assembly process that forms fibers was studied at the QCM gold
electrode surface as pH values were increased from 3 to 7, followed by HRP polymerization
of the fibrils. In this biosensor, as a result of HRP catalysis the self-assembled monomers'
gold surface binding properties (mass) as well as their viscoelastic properties above the crys-
tal surface have changed upon forming self-assembled polymers. This change was detected
through shifts in the frequency,
R
, parameters of the QCM
device, providing a sensitive measure of the time course of the polymerization reaction. As
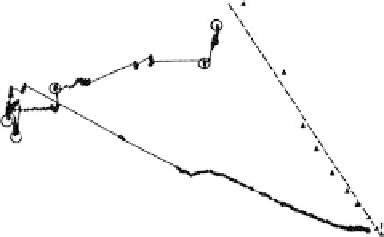
shown in Figure 1.27, in this system prior to polymerization (follow arrows up to point
labeled 2), the frequency decreases as monomer fibril mass is increasingly bound to the gold
QCM electrode, but the motional resistance at the QCM surface has only reached 200
f
, and motional resistance,
.
Consequently, only a low level of energy was dissipated by the self-assembled monomer
DEDT at these pH values. Once fibrillar aggregates were bound to the QCM surface in a
quasiequilibrium state, we initiated polymerization at the points labeled 2-4 by adding a
series of small aliquots of HRP and hydrogen peroxide, as indicated in Figure 1.27.
Enzymatic polymerization resulted in significant changes in the frequency and motional
resistance, especially the latter parameter, indicating that a significantly greater energy was
being dissipated. There was a shift from 200
at the
end of polymerization. These changed values reflected changes in the viscoelastic properties
of the bound and surface proximal fibrillar aggregates as polymerization of monomers pro-
ceeded. A final polymerized state was achieved in which the altered physical properties of
the polymerized fibrillike aggregates made the solution immediately above the gold QCM
surface behave as a Newtonian fluid, producing a nearly pure density-viscosity energy dis-
sipative effect, (
prior to polymerization to nearly 500
)
1/2
, on the measured crystal frequency and motional resistance values.
600
500
t
= 143 h
4
400
3
300
2
1
200
100
Pure elastic mass response
0
0
FIGURE 1.27
A
f
diagram of the time course of binding and HRP polymerization of DEDT monomer (see Figure 1.22) aggre-
gates at pH 7.0. Arrows indicate the time course of the data points starting at the lower right with the
t
R
-
0 point
being the most rightward. At the point labeled 1, HRP was added. At circled points 2, 3, and 4, H
2
O
2
was added.
The final circled time point at 143 h after the initiation of the experiments is also indicated. The
R
-
f
behavior of
a pure elastic mass is indicated by the horizontal line. The
f
points (filled triangles) determined experimen-
tally for a series of increasing concentration sucrose solutions are depicted with the best fit dashed line. This is the
behavior of a Newtonian fluid producing a pure (
R
-
f
values.
Reprinted with permission from Marx, K.A., Zhou, T., Sarma, R. (1999). Quartz Crystal Microbalance Measurement
of Self-Assembled Micellar Tubules of the Amphiphilic Decyl Ester of
D
-Tyrosine and Their Enzymatic
Polymerization.
Biotechnol. Progress
15:522-528.. Copyright (1999) American Chemical Society.
)
1/2
density-viscosity effect on the QCM
R
-