Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Auxiliary electrode
Reference electrode
Working electrode
Multiarray biosensor
Immobilization of the bioreagent
Toxic sample:
pesticides, heavy
metals, phenols, and
bacterial pathogens.
Biological
signals
Transduction
multichannel
Transduction
multichannel
R1
R1
R1
R2
R2
R2
R3
R3
R3
R4
R4
R4
R5
R5
R5
R6
R6
R6
Data processing & quantification
Chemometric analysis
Computational methods
• Identification
• Differentiation
• Classification
Toxic / nontoxic
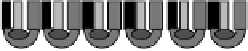
FIGURE 19.1
Schematic diagram of multiarray (bio)sensor system.
(A)
(B)
(C)
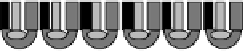
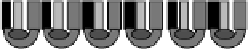
FIGURE 19.2
Examples of sensor arrays used in our laboratory.
are arrays of individual sensors assembled together to form a 96-electrode array. These
have been designed to monitor multiple samples simultaneously and, also, each sensor
could be modified to detect one or multiple analytes. In the last two configurations (B and
C), the sensors are assembled in a format that is compatible with a conventional 96-well
plate. In our laboratory, we have used these sensors for monitoring cell-specific metabolic
activity via electrochemical detection of oxygen consumed by the cells over time and for
cytotoxicity monitoring (12). Table 19.1 is a summary of multiarray sensors described in