Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Haronian and Lewis [99], a color-discriminator developed by Boyer et al. [100], a color-
sensitive artificial retina developed by Frydrych et al. [101] (Chapter 16 by Lensu et al. in
this volume), a photodetector by Xu et al. [102], and by Wang et al. [103] (Chapter 17 by
Wang et al. in this volume).
15.6.3
Specific Ion Sensors Based on the DC Photoelectric Effect
Seki et al. [104] developed an experimental prototype in which the gate region of an ion-
sensitive field effect transistor (ISFET) was coated with a hR layer (Figure 15.21). The design
of this sensor was similar to an earlier one developed by Tanabe et al. [105], who used bR
instead as the light-sensing element. Seki et al. covered the gate region of the ISFET with a
polyvinylbutyral (PVB) resin layer. They then immobilized hR-containing membrane vesi-
cles in the matrix of PVB resin layer. They measured the gate voltage of hR-ISFET directly
with a silver-silver chloride reference electrode. The gate voltage in response to a long
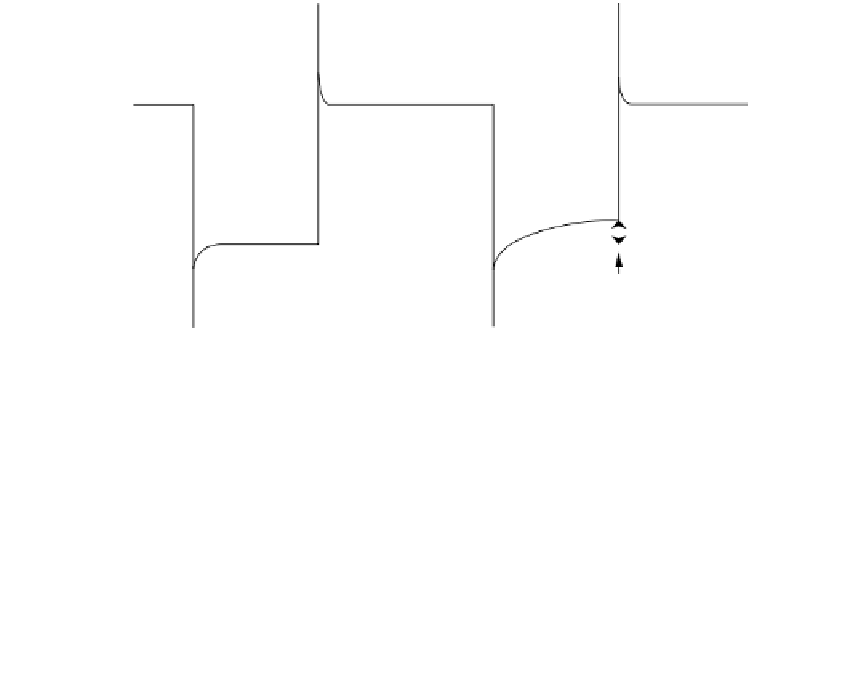
square-wave pulse of light (duration about 2 min) is shown in Figure 15.21A.
Light on
Light on
KCl
mV
∆
V
Light off
Light off
1 min
(A)
10
8
6
4
2
0
0
5
10
15
20
(B)
FIGURE 15.21
An ion-sensitive field effect transistor (ISFET) sensor based on the DC photoelectric effect of hR. hR-containing
vesicles were immobilized on an ISFET. (A) The photovoltage in response to a 3-min square-wave light pulse was
recorded before and after the addition of KCl. (B) The difference
V
shown in (A) was plotted against the Cl
-
concentration. (From Seki, A., Kubo, I. Sasabe, H., Tomioka, H. (1994). A new anion-sensitive biosensor using an
ion-sensitive field effect transistor and a light-driven chloride pump, halorhodopsin.
Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol.
48:205-211.)