Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Mutant
H. salinarum
containing optimized BR protein
Optimal property efficiency range for specific device application
?
?
Wild type
Halobacterium salinarum
?
1
2
3
4
5
Generation of random progeny
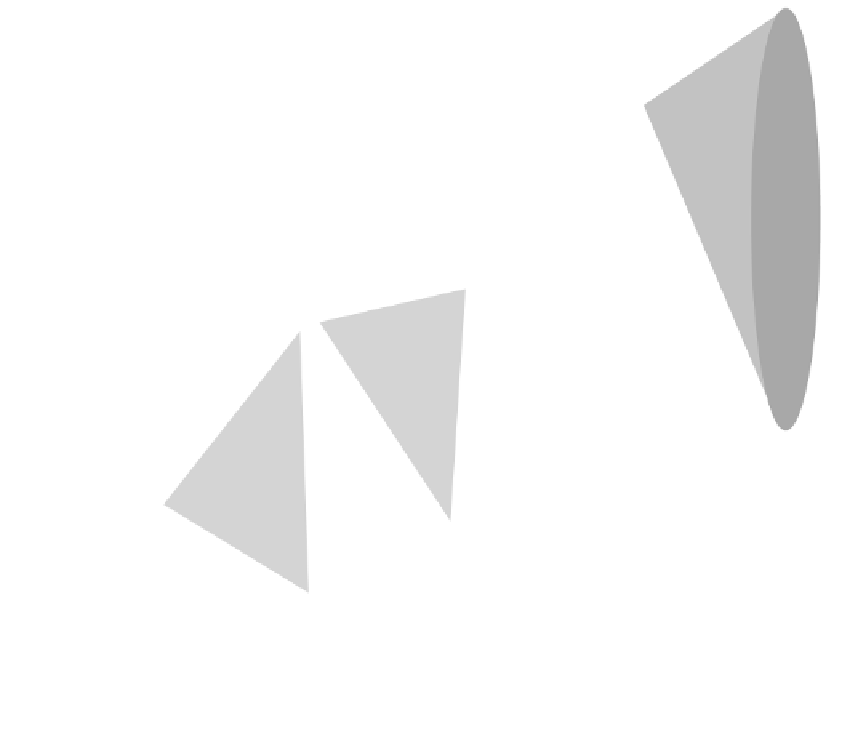
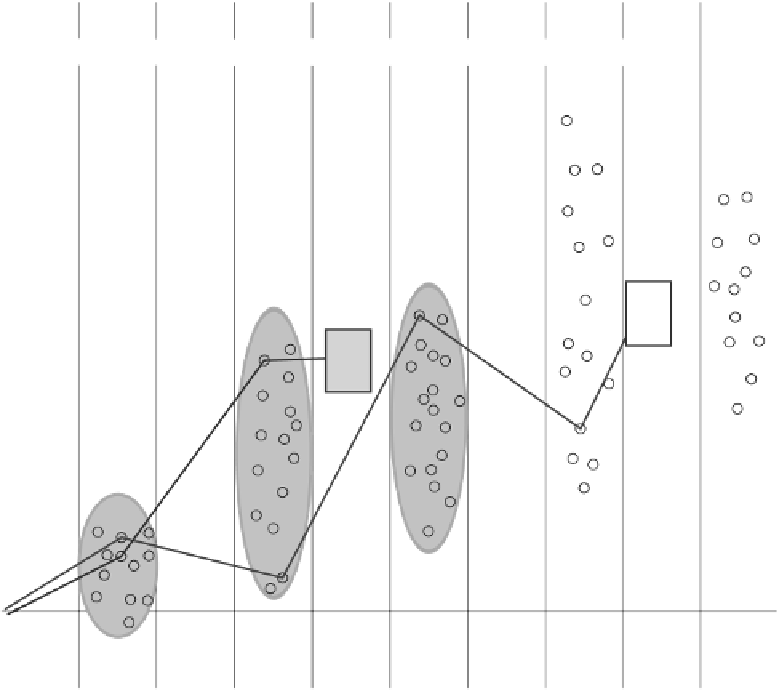
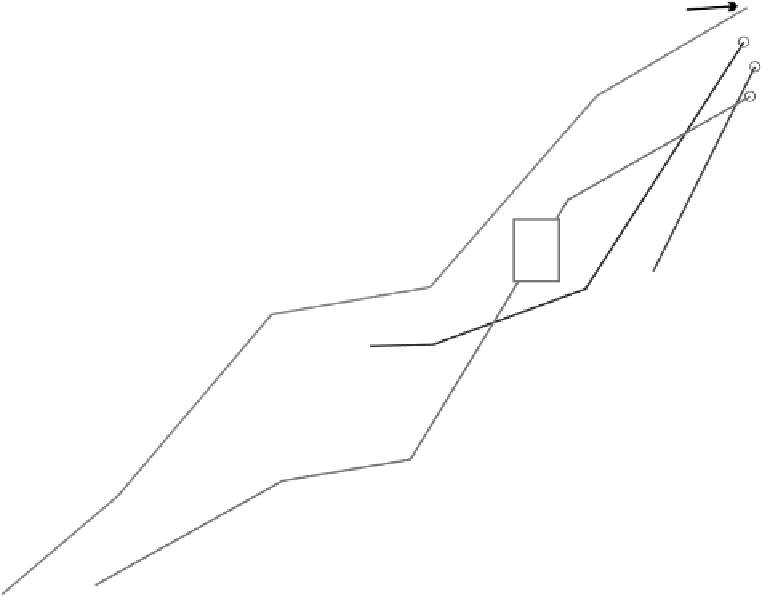
FIGURE 14.3
(See color insert)
Schematic illustration of directed evolution of a bacterial protein toward a predefined goal. The
bold green line indicates the route selected by the researcher, where, based on screening, the strain containing the
most efficient mutant protein of each generation was chosen to parent the next. However, as shown by the ques-
tion marks, other synergistic routes may be possible, but never discovered.
FIGURE 14.4
(See color insert)
(a) Top left: Mutant strains of
H. salinarum
are brought up in 96-well plates and screened for
production of bacteriorhodopsin; each well in the plate is analyzed by a plate scanner that generates a visible
absorption spectrum for each strain, indicating whether the protein is produced (middle left). Top right: BR
mutants are screened for
λ
max
, O-state formation and decay time, and
Q
, a quality factor determining how effi-
ciently the O state is formed (maximum yield in minimum time). The cluster of mutants at the far right of each
plot indicates several site-directed mutants included for comparison. The lower panel (b) illustrates a method by
which flow cytometry could be used to screen for potentially valuable BR strains in vivo, cell by cell, in this case
for efficient production of the branched photocycle. The three-step cell sorting system allows for in vivo high-
throughput photochromokinetic screening. The first stage (1) selects for BR expression and high growth rate. The
second stage (2) selects mutants with high photochemical conversion into the branched photocycle (O
P con-
version). The third stage (3) selects for mutants having efficient photochemical conversion from the branched
photocycle back into the bR state (Q
→
bR conversion). Mutants with desired photochemical characteristics are
automatically deposited onto a single well of a 96-well plate (96WP). Other symbols: GR (grating), CCD (charge
coupled detector), FL (flash lamp), HSDS (high-speed drop selector), BS (beam stop). See Hillebrecht et al.,
Optimization of protein-based volumetric optical memories and associative processors using directed evolution
.
Nanobiotechnology
, 2005.
1
(2): 141-152 for more detail.
→