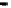Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
O
R
O
H
+ 4H
2
O
[1]
SI
OR
RO
HO
SI
OH
OR
OH
O
O
O
H
O
H
−
4(
n
+1) H
2
O
O
SI
O
(
SI
O
)
n
+
n
[2]
HO
SI
OH
HO
SI
OH
O
O
OH
OH
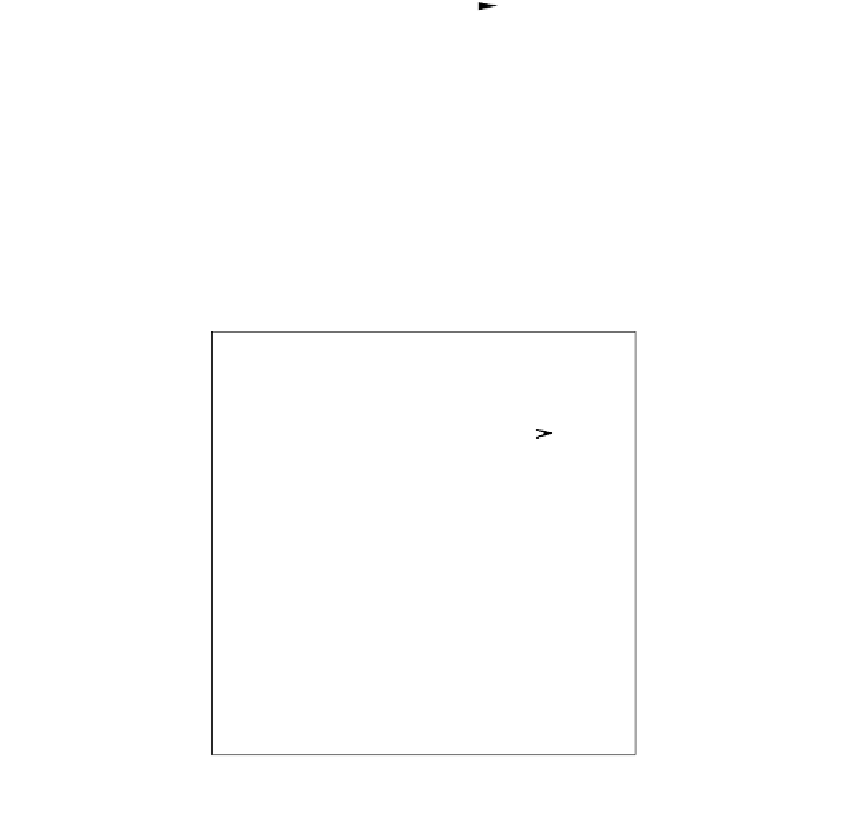
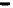
FIGURE 1.8
Reaction scheme leading to the formation of transparent sol-gel glasses at room temperature. In step [1], an
alkoxide is hydrolyzed to form silanol groups (Si-OH) and alcohol (not shown). Subsequent condensation reac-
tions between silanol groups take place in step [2] to produce siloxane bonds (Si-O-Si). Polycondensation events
continue during aging and the sol-gel is then dried to produce a transparent glass. Reprinted from Chen, Z.P.,
Chittibabu, K.G., Marx, K.A., Kumar, J., Tripathy, S.K., Samuelson, L.A., Akarra, J., Kaplan, (1994). Photodynamic
Protein Incorporated in Conducting Polymer and Sol-Gel Matrices: Toward Smart Materials for Information
Storage and Processing. In: Varadan, V.K., ed., Smart Materials and Structures,
Proc. SPIE
, 2189:105-115. With
permission of the International Society for Optical Engineering.
1.5
1.0
1.0
0.5
0.5
0.0
0.0
450
500
550
600
650
700
750
Wavelength (nm)
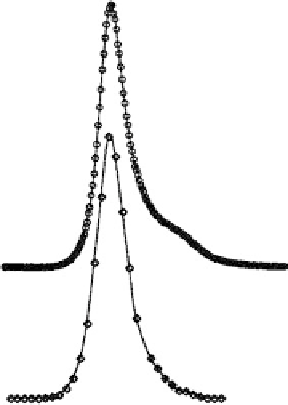
FIGURE 1.9
Fluorescence spectra of PE protein induced by one or two photons in buffer solution. Open circles (upper curve)
are data for two-photon-induced fluorescence, with excitation at 1.06
m. Open diamonds (lower curve) are data
for one-photon-induced fluorescence excited at 490 nm. Reprinted from Chen, Z.P., Kaplan, D.L., Yang, K.,
Kumar, J., Marx, K.A., Tripathy, S.K. (1997). Two-Photon Induced Fluorescence From the Phycoerythrin Protein.
Appl. Optics
36:1655-1659. With permission from the Optical Society of America.
photostable to 3
10
5
repetitions of the two-photon optical experiment, not exhibiting any
loss of intensity of the type that is observed in single photon fluorescence. The measured
two-photon cross-section of phycoerythrin was observed to be 20-fold larger in magnitude
than that of the dye rhodamine 6G. Therefore, there appears to be potential applications