Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Enzyme
redox
center
A
Enzyme
R
R
R
R
SWNT dispersion
X-linker
R
R
R
+
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
Electrode
Electrode
Electrode
Redox polymer
Bare GCE
SWNT-coated GCE
SWNT-coated GCE
Osmium
redox center
B
R
R
R
R
R
SWNT
dispersi
on
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
Electrode
R
R
Redox polymer
R
R
+
R
R
R
Enzyme-treated
SWNT
R
Electrode
R
R
X-linker
Enzyme
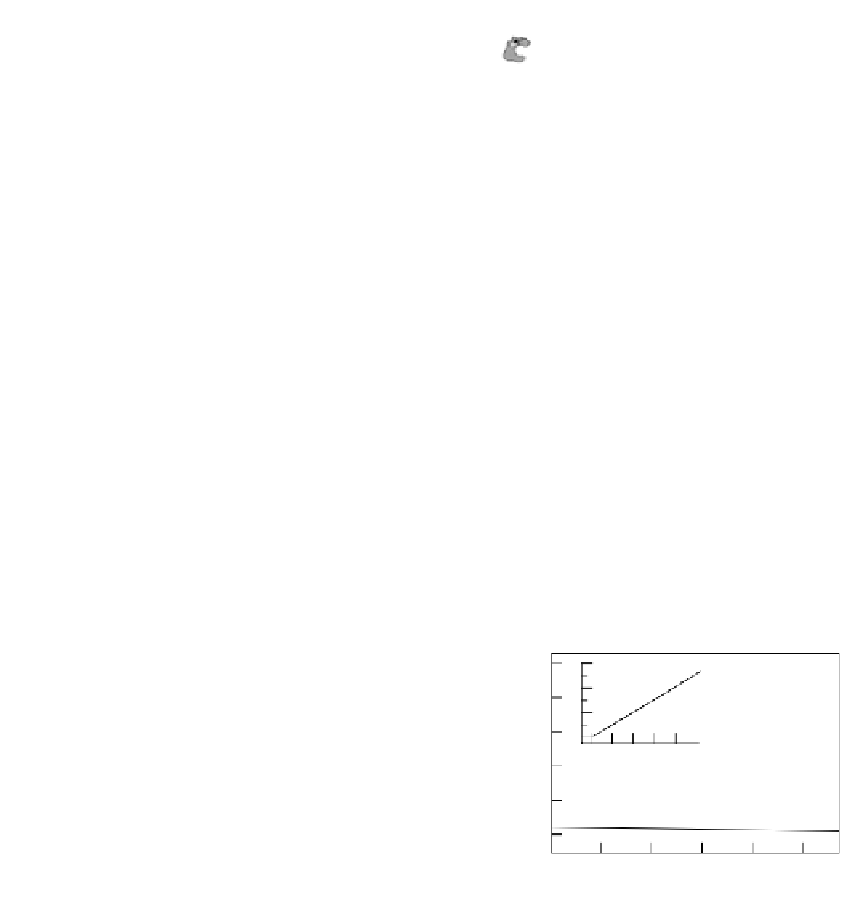
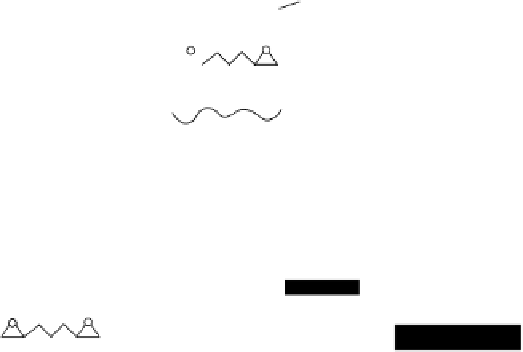
FIGURE 12.16
Schematic illustration of the construction of type A and type B sensors.
(
A) Fabrication of type A sensors in which
a film of SWNTs was first cast onto a bare glassy carbon electrode and allowed to dry, before an aliquot of the
redox hydrogel was cast on top of the SWNT-coated electrode. (B) Fabrication of type B sensors in which SWNTs
were first incubated with an enzyme solution, before they were incorporated into the redox hydrogel. An aliquot
of the redox hydrogel solution containing the enzyme-modified SWNTs was then cast on top of a bare glassy car-
bon electrode. (From Joshi, P. P., Merchant, S. A., Wang, Y., Schmidtke, D. W. (2005). Amperometric Biosensors
Based on Redox Polymer-Carbon Nanotube-Enzyme Composites.
Anal. Chem.,
77(10), 3183-3188.)
10
12
8
4
0
8
d
6
(mM)
01234
4
2
c
b
0
40
a
60
80
100
120
140
Time (S)
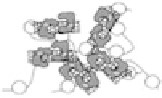
FIGURE 12.17
Left: TEM micrograph of untreated SWCNTs dissolved in 5% Nafion (diluted 10-fold with water), left insets:
AFM tapping-mode height image (size, 10
m; data scale, 100 nm) of SWCNTs and TEM image of Pt
nanoparticles in 5% Nafion (diluted 10-fold with water); middle: TEM micrograph of SWCNT in the presence of
Pt nanoparticles. Middle inset: AFM tapping-mode phase image (size, 1
m
10
m; data scale, 20 nm) of one
SWCNT in the presence of Pt nanoparticles; right: amperometric response for four different electrodes upon sub-
sequent additions of 1 mM glucose solution in 50 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.2) at 0.55 V vs. Ag/AgCl (3 M
NaCl) at 25
m
1
C. (a) GC/GOx, (b) GC/CNT
GOx, (c) GC/Pt
nano
GOx, and (d) GC/CNT
Pt
nano
GOx. Inset
shows calibration curve for glucose concentrations between 0.5
M and 5 mM. (From Hrapovic, S., Liu, Y., Male,
K. B., Luong, J. H. T. (2004). Electrochemical Biosensing Platforms Using Platinum Nanoparticles and Carbon
Nanotubes.
Anal. Chem.,
76(4), 1083-1088.)
glucose analysis (with a detection limit of 0.5 mM and response time of 3 s) compared with
the glassy carbon electrode modified by Pt NPs or CNTs alone.
In addition, despite their catalytic properties, metal NPs can provide a full range of
reactivity with different biomolecules. The biofunctionalized nanocomposite can provide
the unique reorganization ability and high selectivity by attaching specific probes, which
make CNT-NP composites attractive for biosensor application [155]. An electrochemical