Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
Core
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
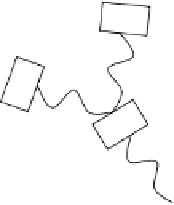
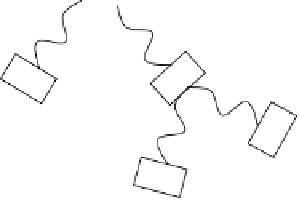
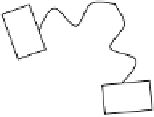
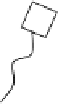
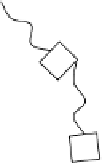
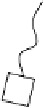
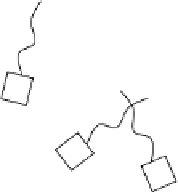
FIGURE 7.4
Cartoon representation of a dendrimeric star-shaped structure. Repeating blocks B emanate from a core to form
the structure. Only one type of representation is shown, and other structures are possible.
external size and internal architecture can lead to the design of interior cavities or chan-
nels with properties different from those on the exterior surface. This enables the possibil-
ity of dendrimers to enclose guest molecules for targeted drug delivery or gene therapy.
Thus, these highly branched dendritic macromolecules are being applied to solubilize
drugs, in DNA biosensors, and in the delivery of targeted oligonucleotide sequences.
Constable et al. (27) have reported on dendrimers containing a metallic core of ruthe-
nium, iron, or cobalt. These macromolecules open possible applications in electrochemical
biosensing. Wendland and Zimmerman (28) produced dendrimers with hollow cores.
Dendrimers with hydrophobic or hydrophilic interiors have also been reported
[Maciejewski (29), Newkome et al. (30)].
Yoon and Kim (31) and others have reported on the synthesis and electrochemistry of
several families of silicon- and nitrogen-based dendritic molecules modified with
organometallic moieties as surface functional groups (32-34). The synthesis of