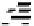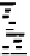Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
6.3.2
Responses to Toxins
Given the histotypic responses observed with pharmacological studies, it is not surprising
that the same is seen with toxins. Extensive data have been gathered with tetrodotoxin,
botulinum toxin A, tetanus toxin, and the nerve gas hydrolysis products methyl phos-
phonate, pinacolyl methylphosphonate, and isopropyl methyl phosphonate. Whereas
tetrodotoxin and botulinum toxin revealed rapid and slow (respectively) activity shut-off
in the nanomolar and picomolar ranges (unpublished), the nerve gas hydrolysis products
were found non-toxic, as millimolar concentrations were required for partial activity
decreases [5]. Methyl phosphonate had no effect on network spike production up to 5 mM.
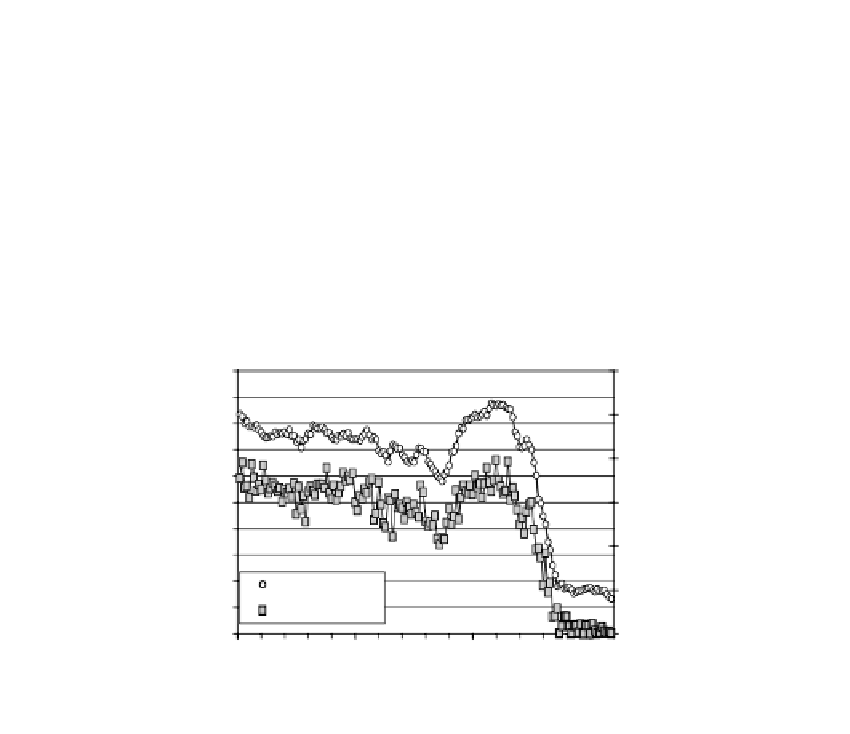
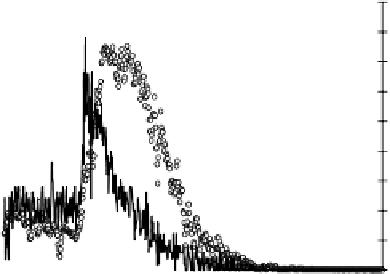
Figures 6.11 and 6.12 show network responses to tetanus and botulinum toxins. The
tetanus toxin data show tissue specificity with an expected greater effect on spinal net-
works. Both the time course of activity changes and the eventual involvement of all the
neurons in the network agree well with the published data. Williamson et al. [26] investi-
gated the effect of this toxin on the release of radiolabeled glycine and glutamate, followed
over time intervals corresponding to the early phase of convulsant activity through the later
phase of electrical quiescence. Approximately 90 min after toxin application, the release of
glycine was blocked and glutamate release increased to twice the normal. Blockage of
1600
45
1nM TetTox
Mean spike rate
Mean burst rate
40
1400
35
1200
30
1000
25
800
20
600
15
400
10
200
5
0
0
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
TetSC1 3/20/01
Time (min)
Spinal cord
200
30
1nM TetTox
180
25
160
140
20
120
100
15
80
10
60
40
Mean spike rate
Mean burst rate
5
20
0
0
0
50
100
150
kt004 4/12/01
Time (min)
Frontal
cortex
FIGURE 6.11
Responses of spinal and frontal cortex networks to tetanus-toxin (1 nM). Whereas the spinal network shows
strong excitation after a 30-min delay followed by gradual decline to catastrophic failure in 200 min, the frontal
cortex network responds with weak excitation after 25 min followed by catastrophic network failure in 70 min.