Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
influence sorting? During initial Trk activation and subsequent endocytosis,
signaling molecules are rapidly attracted to docking sites on activated Trk
receptors (
Chowdary, Che, & Cui, 2012
). Does the organization or
strength of preendocytic Trk signaling influence vesicle sorting into
specific endosomal compartments? Though there is debate on the
number of neurotrophin molecules per signaling endosome under
differing experimental paradigms (
Chowdary et al., 2012
), the number of
neurotrophins likely differs per signaling endosome from one to many.
By tracking quantum dot-NGF (QD-NGF) retrograde transport in
compartmentalized sympathetic neuron axons,
Cui et al. (2007)
argue
that the “majority” of signaling endosomes contain only a single
QD-NGF. However, in these experiments, the number of QD-NGF
particles per endosome varied greatly depending on concentration and on
their method of visualization, that is, transmission electron microscopy
versus “pseudoTIRF” microscopy (compare 2 nM,
Figs. 2.4 and 2.5
)
(
Cui et al., 2007
). Under low concentrations, most QD-NGF endosomes
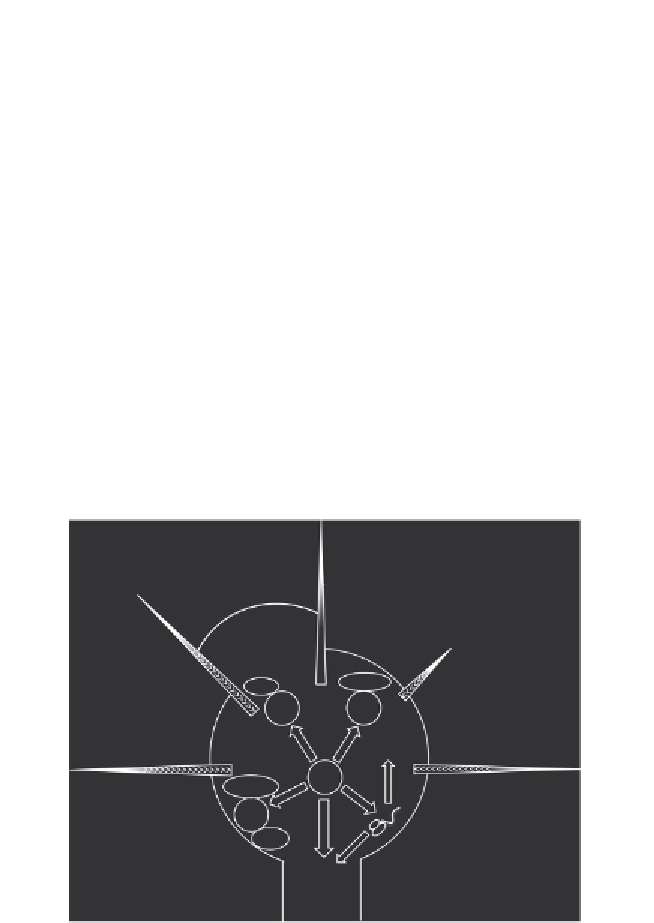
Filopodial
protrusion
Lamellar
protrusion
Cdc42
Rac
SE
SE
Cytoskeletal
remodeling
SE
PTPD1
SE
CAM
cycling
Src
Local
translation
Retrograde
signaling
Neurite shaft
Figure 2.4 Signaling endosomes (SE) influence growth cone activities by localizing cy-
toskeletal effectors. Rac and Cdc42 localization influences various activities including
lamellar and filopodial protrusion. Protein-tyrosine phosphatase (PTPD1) and Src local-
ization can influence adhesion assembly, disassembly, and signaling. Signaling
endosome-regulated translation in the growth cone can influence retrograde signaling,
including long-distance transcription factor signaling, as well as the local production of
proteins necessary for cytoskeletal remodeling underlying growth cone motility.