Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 2.3
Language equation
with respect to a composition
topology with three
components
inherits the feature of being U -progressive. If S is not U -progressive, then denote
by
Prog
.S / the set obtained from S by deleting each string ˛ such that, for some
u
2
U , there is no o
2
O for which ˛.
u
;o/
2
S .
Proposition 2.15.
If Prog
.S /
¤;
, then the language Prog
.S /
is the largest
U
-progressive solution of the equation
A
X
C
.
If Prog
.S /
D;
, then the equation
A
X
C
has no
U
-progressive solution.
2.2.2
Language Equations Under Parallel Composition
Given the pairwise disjoint alphabets I; U; O, a language A over alphabet I
[
U ,
and a language C over alphabet I
[
O, consider the language equation
A
˘
X
C;
(2.4)
or,
A
˘
X
D
C:
(2.5)
Definition 2.2.2.
Given the pairwise disjoint alphabets I; U; O, a language A over
alphabet I
[
U and a language C over alphabet I
[
O, language B over alphabet
U
[
O is called a
solution
of the equation A
˘
X
C iff A
˘
B
C .
Given the pairwise disjoint alphabets I; U; O, a language A over alphabet I
[
U
and a language C over alphabet I
[
O, language B over alphabet U
[
O is called
a
solution
of the equation A
˘
X
D
C iff A
˘
B
D
C .













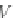





Search WWH ::

Custom Search