Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
V
1
time
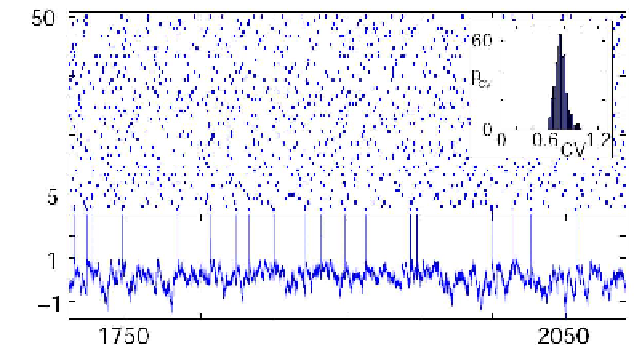
Fig. 13.6. Balanced irregular neural activity. Upper part shows irregular spiking dynamics char-
acteristic for the balanced state. Lower part displays the normalized, highly irregular membrane
potential of neuron 1. Inset displays the distribution of the coecients of variation of the neurons'
spike trains. This dynamics is stable against small perturbations, the irregularity does not result
from chaos. (Modied from [74].)
rons in the network, see, e.g., [168], (ii) as non-periodic states with periodic oscilla-
tory network rate dynamics (e.g. splay states [24, 25, 160] and cf. section 13.4.2) and
(iii) and as aperiodic irregular states with constant network rate and no apparent
coordination of spike times [24, 163].
The balanced state constitutes a key example of asynchronous irregular spiking
as it is considered as a possible ground state of cortical activity. In such a state, ex-
citatory and inhibitory synaptic input to each neuron balances such that the average
membrane potential is sub-threshold and large uctuations generate spikes at low
rate and at seemingly random times [24, 162, 163]. Whereas the original assump-
tion was that chaotic dynamics causes these apparently random spiking sequences,
it was recently found ([73, 74], (cf. also [167]) that dynamics with the same irreg-
ularity is prevalent also in systems which do not exhibit chaotic, but rather stable
microscopic dynamics. This raises the question which dynamical features actually
generate asynchronous irregular spiking dynamics characteristic for the balanced
state. A further question of current research is how balanced irregular activity may
persist after a transient external stimulus has initiated it [57, 58, 84].
In theoretical investigations, the analysis of asynchronous states may also serve
as a starting point to reveal mechanisms that underlie more coordinated neural
activity by studying bifurcations away from asynchrony, see, e.g., [59].
13.5. Precise Timing in Recurrent Networks
As some results presented in the previous section already suggest, patterns of spikes
that are precisely timed and coordinated among neurons may also emerge in the