Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
Planning for Plant-Growth Needs
Annuals vs. Perennials
Row or Intensive Plant Spacing
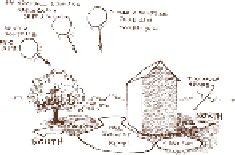
WORKING WITH THE SUN
When you picked a community garden site, it's likely that you chose
the best possible location for
maximum sun exposure, but there are times—due to trees, buildings, or other obstructions—when all
areas of the community garden will not get full coverage. It is important to make gardeners aware of
crops that can work in the conditions specific to their plot location. And, sometimes, it takes a season
in the garden to see the light patterns and how they impact a particular area. If a bed is in a potentially
shady spot, this information will be useful to new gardeners, so they don't get discouraged when they
can't grow their prized, sun-loving crop. Many popular garden vegetables, like tomatoes and peppers,
need 6 to 8 hours of full sun to reach maturity. But there are lots of other crops that can grow success-
fully with limited sun.
Location, Location, Location
Crops for Part Sun (2 to 4 hours)
Crops for Dappled Sun
Chives
Cilantro
Leafy greens
Parsley
Peas
Scallions
Beet greens
Cabbage (small headed varieties)
Endive
Leeks
Lettuce
Radishes
Spinach
Turnip greens
Plan your garden to take best advantage of available sun year-round.
MAKING THE MOST OF SMALL SPACES
Depending on the layout of your community garden, individual
gardeners may or may not have end-
less room to plant everything they want to grow. Particularly with individual raised-bed allotment gar-