Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(e.g., in a building or in a mine), the only measurements necessary to determine the unattached
fraction (and to infer the average aerosol surface area) are those described earlier—a diffusion
battery followed by a backing ilter and an open face ilter operated in parallel. The alpha activity
from
218
Po on each of these three collectors is then measured and used with appropriate calibration
factors to yield the unattached fraction (Figures 16.3 through 16.9).
Results of the calculation showed that
1. For a constant unattached fraction, f, aerosol particles surface area, practically speaking,
(in the range of measurements errors) does not depend on particle size in the nanometer
range from 2 to 100 nm in diameter.
2. The presented idea for assessment of the surface area will work for polydisperse nanometer-
sized particles.
3. This method will not be sensitive to very small individual particles, because its contribu-
tion to the general surface area is proportional to the square of their diameter.
100
80
60
40
20
0
10
-6
10
-5
Aerosol surface area concentration, s(cm
-1
)
10
-4
10
-3
10
-2
10
-1
1
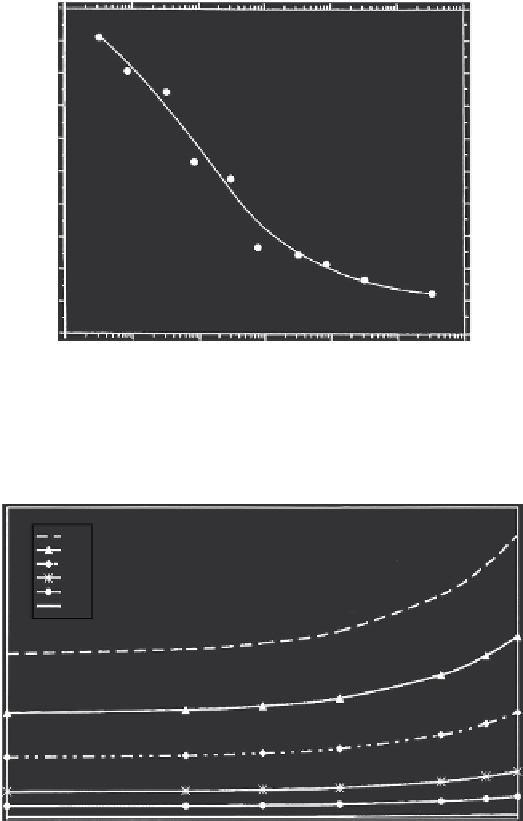
FIGURE 16.3
Unattached fraction of
218
Po, f vs. aerosol surface area concentration.
Correlation between aerosol surface area and unattached radium A (
218
Po)
1.E- 06
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
0.95
0.95
1.E- 06
8.E- 07
6.E- 07
4.E- 07
2.E- 07
0.E+ 00
1.0.E- 07
1.0.E- 06
r (cm)
1.0.E- 05
FIGURE 16.4
Relationship between particle surface area and particle radius.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search