Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
water-methanol (20% MeOH), neutral or acid solutions with GA concentrations ≤0.5 mM. In 50%
water solution, micellation does not occur.
The conclusion about small-size associates formation is based on the fact that the dependence of
GA mole fraction in micellar state on the concentration does not drastically change in the MCC range.
The study of water solutions by small-angle x-ray scattering method showed that at the concen-
tration of about 1.0 mM glycoside forms rod-like associates with the radius ∼1.4 nm and length up
to 60 nm. The associates are stabilized by intermolecular hydrogen bonds.
11.2.1.2 Complexes of Pharmacons with Glycyrrhizic Acid
The pioneering works on complexation are Soltesz et al. (1963) and Krasova et al. (1978), where the
solubilizing effect of glycyrrhizic acid and its monoammonium salt, glycyrrham, was investigated
for a series of water-insoluble pharmacons. In the earlier-stated works as well as in Sasaki et al.
(1988), it was demonstrated that it is possible to obtain water solutions of practically water insoluble
antibiotics such as oxytetracycline, nystatin, actinomycin C, corticosteroids such as hydrocortisone
and prednisolone, and sulfazine, a sulfanilamide drug. GA demonstrates solubilizing properties at
concentrations higher than MMC (Krasova et al., 1978). It should be noted that none of the earlier-
mentioned works discusses the ability of glycyrrhizic acid to form complexes with pharmacons.
For the irst time the issue was discussed in Tolstikov et al. (1990), where GA complexes were
called new carriers for drugs. In earlier studies, the solution method of complex synthesis prevailed.
Nowadays, the method of mechanochemical solid-phase synthesis is employed to obtain the com-
plexes with water-insoluble medicines; it allows achieving an even higher solubility compared to
liquid-phase synthesis (Dushkin et al., 2001).
The mechanochemical processing is performed in an AGO-2 planetary mill. Processing routine:
acceleration of grinding bodies, 60 g; mass of processed mixture, 3 g; cylinder size, 40 mL; grinding
bodies—steel balls, 6 mm in diameter; load size, 75 g. Time of processing ranges from 3 to 10 min.
A longer processing may lead to partial chemical decomposition of samples, while a shorter pro-
cessing period may result in insuficient sample homogenizing.
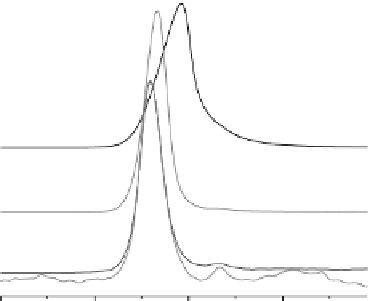
After the mechanochemical processing, the water solutions of GA were characterized by the
method of gel-chromatography (Figure 11.18). In all ranges of studied concentrations (0.0001-0.5
wt.%), peaks of high molecular formations, with molecular mass of ∼46-67 kDa, are observed,
while the molecular mass of GA amounts to 836.96 Da. It has been established that glycyrrhi-
zic acid is almost fully self-associated into micellae, the most stable ones being the micellae
with MM = ∼66 kDa, consisting of almost 80 GA molecules (Dushkin et al., 2010).
4
3
2
1
6
7
8
9
MNH
FIGURE 11.18
Gel-chromatograms of GA solution. 1, Concentration in the tested solution—0.001% weight;
2, 0.01%; 3, 0.1%; 4, 0.5%.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search