Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
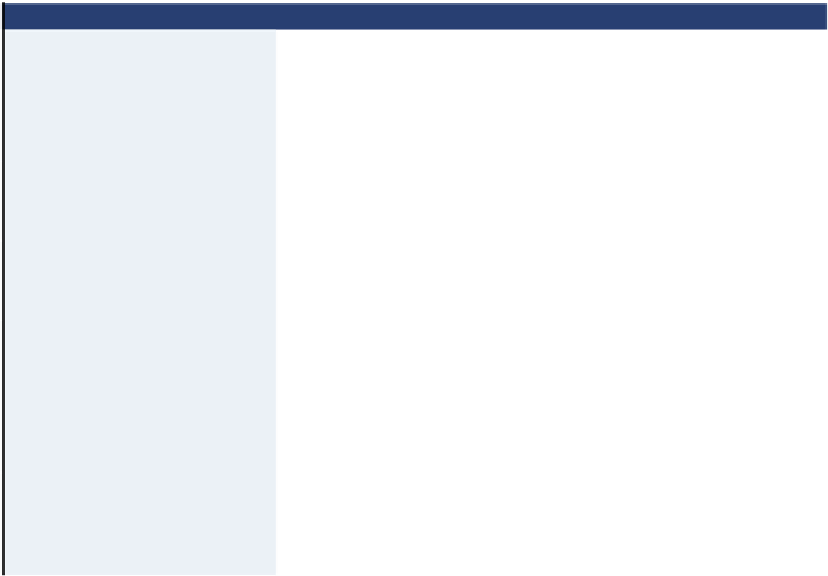
Table 2.3. Examples of Bacterial Isolates That Partially Dechlorinate PCE to TCE or cis-DCE
PCE Dechlorinating Isolate
Dechlorination Activity
Reference
Dehalobacter restrictus
PCE to cis-DCE
Holliger et al.,
1998
;
Wild et al.,
1996
Desulfuromonas chloroethenica
PCE to cis-DCE
Krumholz et al.,
1996
;
Krumholz,
1997
Desulfuromonas michiganensis
PCE to cis-DCE
Sung et al.,
2003
Sulfurospirillum multivorans
PCE to cis-DCE
Luijten et al.,
2003
;
Neumann et al.,
1994
Sulfurospirillum halorespirans
PCE to cis-DCE
Luijten et al.,
2003
Geobacter lovleyi
PCE to cis-DCE
Sung et al.,
2006a
Desulfitobacterium sp. strain
PCE-S
PCE to cis-DCE
Miller et al.,
1997
Desulfitobacterium hafniense
strain TCE1
PCE to cis-DCE
Gerritse et al.,
1999
Desulfitobacterium hafniense
strain Y51
PCE to cis-DCE
Suyama et al.,
2001
Desulfitobacterium hafniense
strain JH1
PCE to cis-DCE
Fletcher et al.,
2008
Desulfitobacterium sp. strain
PCE1
PCE to TCE
Gerritse et al.,
1996
Desulfitobacterium sp. strain
Viet1
PCE to TCE
L¨ ffler et al.,
1997b
;
Tront et al.,
2006
Compared with
Dehalobacter
, these isolates exhibited more versatile metabolisms and
used a greater variety of electron acceptors and electron donors for growth. In contrast to
Dehalobacter
strains, PCE-dechlorinating
Desulfuromonas
isolates cannot use hydrogen but
use several reduced organic compounds, including acetate as electron donors (Krumholz et al.,
1996
; Sung et al.,
2003
).
Geobacter lovleyi
strain SZ uses both acetate and hydrogen as electron
donors and was the first PCE-dechlorinating isolate within the
Geobacter
group. Several
members of this bacterial group are well known for their ability to reduce metals and radio-
nuclides and
Geobacter lovleyi
reduces PCE and hexavalent uranium simultaneously, suggest-
ing that organisms of this type are promising for remediation of radionuclides and PCE at
mixed waste sites (Sung et al.,
2006a
).
Sulfurospirillum multivorans
(formerly
Dehalospirillum
multivorans
) is a well-studied PCE dechlorinator because this organism is easy to culture and
high biomass yields facilitate biochemical studies (John et al.,
2009
; Luijten et al.,
2003
;
Neumann et al.,
1996
; Scholz-Muramatsu et al.,
1995
). Several
Desulfitobacterium
isolates
were described to dechlorinate PCE, typically to
cis
-DCE as the dechlorination end product, but
Desulfitobacterium
sp. strains PCE1 and Viet1 reduce PCE to TCE. This is an interesting
observation because the characterized PCE reductive dehalogenases (RDases) from
Sulfuros-
pirillum
,
Dehalobacter
and
Desulfitobacterium
reduce PCE to
cis
-DCE (Maillard et al.,
2003
;
Miller et al.,
1998
; Neumann et al.,
1996
; Suyama et al.,
2002
), suggesting that strain PCE1 and
strain Viet1 possess unique PCE-to-TCE reductive dehalogenase enzyme systems. In any case, a
diverse bacterial group contributes to PCE-to-
cis
-DCE dechlorination but the microbes con-
tributing to dechlorination past
cis
-DCE remained elusive.















Search WWH ::

Custom Search