Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
cbrA
(Strain CBDB1)
tceA
(Strain 195)
ori
HPR2
HPR1
vcrA
(Strain VS)
orange
= % blastn
identity to BAV1
pink
= % blastn
identity to GT
blue
= % blastn
identity to VS
green
= % blastn
identity to 195
bvcA
(Strain BAV1)
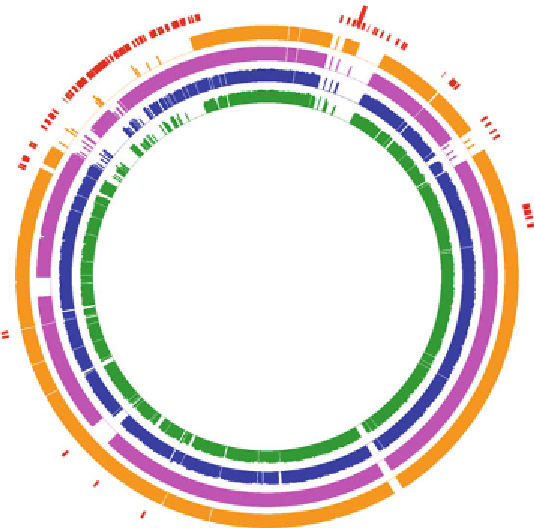
Figure 2.4. Circular maps of Dhc genomes of strains BAV1, GT, VS and 195 with the genome of
CBDB1 (not depicted) serving as the reference. The non-contiguous red slashes correspond to
RDase genes in the genomes of all five Dhc strains. The outermost ring represents the blastn
alignment of 1,000 bp blocks of strain CBDB1 to strain BAV1. The second, third and fourth rings
represents alignments of the genomes of strains GT, VS and 195 with CBDB1, respectively. The
height of the bars indicates blastn similarity to the corresponding gene in strain CBDB1 genome.
Indicated by the black arcs are the High Plasticity Regions (HPRs) on either side of the origin of
replication. These HPRs contain the majority of RDase genes and distinguish reductive dechlori-
nation functionality of the different Dhc strains. tceA, bvcA and vcrA encode chlorinated ethene
RDases and cbrA encodes a chlorobenzene RDase. Note that bvcA, a gene implicated in VC
reductive dechlorination, is located in the core genome outside the HPRs in strain BAV1 rdh
abbreviates reductive dehalogenase homologous genes.
host (McMurdie et al.,
2007
). The mechanisms contributing to RDase gene mobilization and
transfer are unclear but the genome analysis provides some hints. A prophage is present in the
strain 195 genome and microscopic observations suggested the presence of phage (bacterial
viruses) in pure cultures of strain BAV1 (Helton et al.,
2008
; Ritalahti et al.,
2007
). Phages are
important vehicles of gene transfer and may play roles in RDase gene mobilization between and
within
Dhc
genomes.
A striking aspect of the sequenced
Dhc
genomes is the presence of multiple RDase genes
ranging from 11 in strain BAV1 to 36 in strain VS (Table
2.5
), highlighting the specialization
towards reductive dechlorination.
Another shared feature of the sequenced
Dhc
genomes is the presence of five distinct
hydrogenase gene clusters, which are highly similar in sequence and organization in all
sequenced
Dhc
genomes. Hydrogenase enzyme systems catalyze the reversible oxidation of
hydrogen to two protons and two electrons. Hydrogen is the required electron donor for
Dhc,










Search WWH ::

Custom Search