Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
these dynamics were consequence of the abandonment of traditional activities or the
increase in urbanised areas (Figure 4 and Table 3).
We observed few changes in the study area, indeed, 79.5% of the Park's territory had
undergone no change. The total area affected by some type of change from 1975 to 2009 is
10,852.7 ha. Within this changing area, the most significant dynamics were new pastures
(29.8%) and forest encroachment (26.6%). Scrub encroachment represents 19.5% and urban
development processes 15.7%. New crops represent only 8.8% and occur in the southern
sector of the Park (Table 4).
2009
Rocky
areas
with
scrub
and trees
Forest
Scrub
Pastures
Croplands
Reservoirs
Urban
Forest
NCh
SE*
AA
URB
Scrub
FE
NCh
AA
URB
Pastures
FE
SE
NCh
NC
URB
Croplands
FE
AA
NCh
URB
Rocky areas
with scrub
and trees
FE
SE
NCh
URB
Reservoirs
SE
NCh
URB
Urban
NCh
* This case is referred to forest cleared for livestock farming, a traditional use in Mediterranean areas.
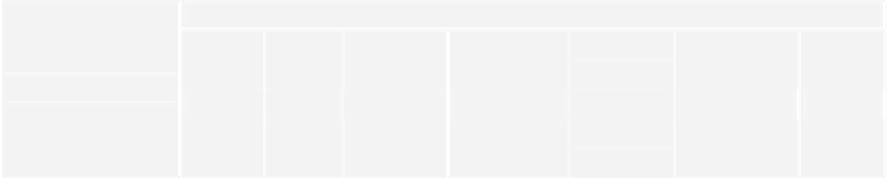
Table 3.
Territorial dynamics from 1975 to 2009. FE: Forest Encroachment; SE: Scrub Encroachment;
AA: Agricultural Abandonment; NC: New Crops; URB: Urban Development; NCh: No Change.
ha
% PNA
% change
% dynamics
FE
2,884.1 5.4 26.6 3.0
SE
2,076.7 3.9 19.5 2.1
AA
3,235.9 6.1 29.8 3.3
NC
955.1 1.8 8.8 1.0
URB
1,700.9 3.2 15.7 1.7
NCh
42,081.8 79.5 43.1
Table 4.
Total surface of each dynamic and percentage area over PNA, change and dynamics areas
These dynamics clearly showed the most dynamic sectors (mainly associated with urban
development) that are located in the South of the PNA, close to the city of Madrid and to the
main communications networks In contrast, the mountainous area located at North
presented fewer changes which are associated with natural dynamics (forest and scrub
encroachment).