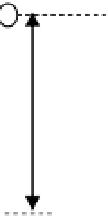Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
T
h
L
h
O.P
.
h
Figure 22.
The diagram for the target height
computing.
6. Inertial Explorer post-processing software for the final perfection of
the MSM accuracy data
Waypoint Products Group's
Inertial Explorer
post-processing software suite integrates rate
data from six degrees of freedom IMU sensor arrays with GNSS information processed with
an integrated GNSS post-processor (same as GrafNav's). Inertial Explorer use strapdown
accelerometer (Δν) and angular rate (Δθ) information to produce high rate coordinate and
attitude information from a wide variety of IMUs.
(Kennedy S. NovAtel Inc., Canada &
Hinueber E., iMAR GmbH, 2005)
Inertial Explorer implements either a loose coupling of the GNSS and inertial data or tightly
coupled (TC) processing that uses GPS carrier phase to limit error during periods where
satellite tracking is limited or variable (even if only 2 or 3 satellites are visible). It is
important to time-tag the inertial measurements to the GPS time frame during the data
collection process. Proper synchronization is vital. Otherwise, the IMU data will not process.
In NovAtel's SPAN system, IMU data is automatically synchronized and the Inertial
Explorer's GNSS decoder automatically extracts the IMU data.
7. Conclusions
In order to increase up to 200 - 300 meters, the distance up to which the sighted targets from
the terrain can be positioned, it resorts to the use of a single digital camera of high resolution
in a fixed montage on a lab vehicle, instead of two cameras which usually are used in the
case of classical stereo photogrammetric systems and for which the measurement basis is
limited by the montage distance between the two cameras on the lab vehicle, respectively by