Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 9.1 The eight pairs of pointers in the micronuclear actin I
gene in
Sterkiella nova
.
Pointers in 5' of MDS
MDS
Pointers in 3' of MDS
GGAGTCGTCAAG (P3)
3
AATC (P4)
AATC (P4)
4
CTCCCAAGTCCAT (P5)
GCCAGCCCC (P6)
6
CAAAACTCTA (P7)
CTCCCAAGTCCAT (P5)
5
GCCAGCCCC (P6)
CAAAACTCTA (P7)
7
CTTTGGGTTGA (P8)
AGGTTGAATGA (P9)
9
3 TAS
CTTACTACACAT (P2)
2
GGAGTCGTCAAG (P3)
5 TAS
1
CTTACTACACAT (P2)
CTTTGGGTTGA (P8)
8
AGGTTGAATGA (P9)
into its macronuclear form: two ld excisions, a dlad excision, an ld excision, a
dlad excision, and, finally, two hi excisions [10].
Assembly of the Macronuclear Molecule Encoding
α
Telomere
Binding Protein
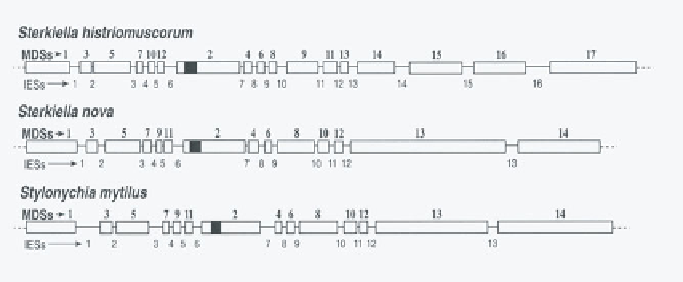
In the actin I gene the MDSs appear to be scrambled in no particular order. In
the micronuclear gene encoding
α
α
TP) in three sti-
chotrich species, the MDSs are scrambled in a predominantly odd/even pattern,
with no inverted MDSs (Figure 9.24).
Sterkiella nova
and
Stylonychia mytilus
have identical patterns with the MDS order: 1-3-5-7-9-11-2-4-6-8-10-12-13-
14, although the corresponding IESs in the two organisms are different in size
and sequence and have migrated, which changes the sizes of MDSs [12].
telomere binding protein (
Figure 9.24
Diagrams of the micronuclear
α
TP gene in three stichotrichs. Macro-
nuclear destined elements (MDSs) are open blocks, internal eliminated segments
(IESs) are lines between blocks, and introns are dark blocks (in MDS 2). From
Prescott et al. [12].