Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Most genes in most organisms are interrupted by noncoding DNA sequences
called introns. When a gene is transcribed into an RNA transcript, introns are
transcribed as part of the transcript. Intron sequences are then spliced out of an
RNA transcript to yield a messenger RNA molecule (mRNA) that is a faithful
copy of the coding segments (exons) of the gene. The significance of introns
is only partially understood; the transcripts of some genes can be processed in
alternative ways so that different combinations of exons are spliced, creating
different mRNA molecules that encode different protein products.
Stichotrich genes are intron-poor; only about 18% of the genes contain in-
trons. However, their germline genes are interrupted by another kind of noncod-
ing DNA called
internal eliminated segments
, or IESs. Unlike intron sequences,
IESs are not transcribed, but are removed from DNA during conversion of mi-
cronuclear genes to macronuclear genes. Most IESs are short (less than 100 bp)
and can be any sequence of A, T, G, and C bases, although they are particularly
rich in A and T bases. IESs divide a gene into segments called
macronuclear
destined segments
, or MDSs. Some micronuclear genes contain a single IES
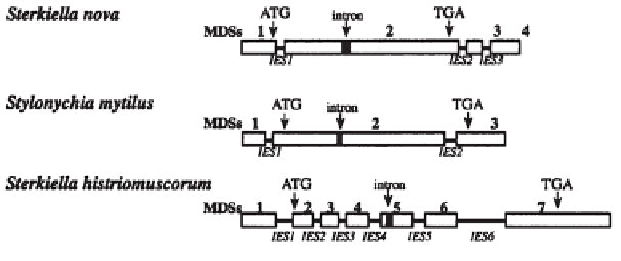
and therefore two MDSs. The gene encoding
TP)
in
Sterkiella nova
contains three IES of 32, 34, and 39 bp, respectively (Figure
9.11), dividing the micronuclear gene into four MDSs [9].
The micronuclear gene encoding
β
telomere binding protein (
β
TP in another species,
Sterkiella histri-
omuscorum
is interrupted by six IESs, creating seven MDSs (Figure 8.11). One
IES is in the 5' leader segment that precedes the coding region of the gene, and
the other five interrupt the coding region. (The coding region is delimited by
the start triplet codon, ATG, and the stop triplet codon, TGA.) Leader segments
generally contain base sequences required to regulate transcription of the gene.
Extrapolation from the IES numbers in 10 different micronuclear genes that
β
Figure 9.11
Diagram of the micronuclear
β
TP gene of
Sterkiella nova
,
Sterkiella
histriomuscorum
, and
Stylonychia mytilus
. Macronuclear destined segments (MDSs)
are open blocks connected by lines (internal eliminated segments). The intron is a
filled (dark) block. ATG is the translation start codon, and TGA is the stop codon.