Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
µ
g/g
16 EPAPAH = 19 700
45 TPAH = 83 700
14 K
Weakly
pyrogenic
A
High volatile
bituminous coal
7K
Ret
Ret
Petrogenic
Petrogenic
na
na
0
µ
g/g
16 EPAPAH = 4820
45 TPAH = 35 800
4500
Petrogenic
B
Coal distillate
generation
temperature
1000 °C
2250
na
na
0
µ
g/g
16 EPAPAH = 358 000
45 TPAH = 470 000
140 K
C
Strongly
pyrogenic
Coal tar
generation
temperature
500 °C
70 K
na
na
0
g/g
µ
16 EPAPAH = 301 000
45 TPAH = 382 000
120 K
Strongly
pyrogenic
D
Coal tar
generation
temperature
1000 °C
60 K
na
0
µ
g/g
16 EPAPAH = 8100
45 TPAH = 12 100
9000
E
Strongly
pyrogenic
Coke
generation
temperature
1000 °C
4500
na = not analyzed
in these samples
na
na
0
PAH analytes
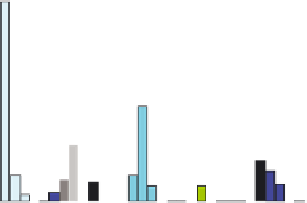
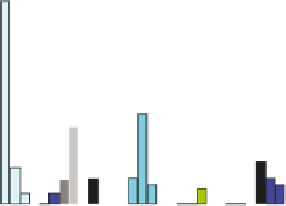
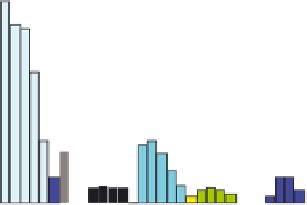
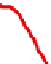
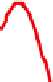
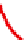
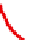
Figure 11.4.4. PAH profiles of high-volatile bituminous coal under various states of thermal exposure: (A) the
high-volatile bituminous coal contains weakly pyrogenic and petrogenic PAHs plus retene and hopane, (B) coal
distillates formed at 500°C (not shown) and 1000°C, respectively, contain nearly identical mixtures of alkylated
two- to four-ring PAHs, (C) and (D) coal tars formed at 500 and 1000°C, respectively, in a coke oven contained
nearly identical mixtures of two- to six-ring pyrogenic PAHs. The passage of the gaseous coal distillate through a
hot-coke bed and contact with oven walls are thought to catalyze the transformation of saturated to aromatic
hydrocarbons with little sensitivity to temperature in the range of 500
-
1000°C, and (E) coke generated at 1000°C.